Reservoir competence of vertebrate hosts for Anaplasma phagocytophilum
- PMID: 23171835
- PMCID: PMC3557888
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1812.120919
Reservoir competence of vertebrate hosts for Anaplasma phagocytophilum
Abstract
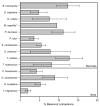
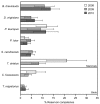
Fourteen vertebrate species (10 mammals and 4 birds) were assessed for their ability to transmit Anaplasma phagocytophilum, the bacterium that causes human granulocytic anaplasmosis, to uninfected feeding ixodid ticks. Small mammals were most likely to infect ticks but all species assessed were capable of transmitting the bacterium, in contrast to previous findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential vertebrate reservoir hosts and invertebrate vectors of Anaplasma marginale and A. phagocytophilum in central Spain.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005 Winter;5(4):390-401. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2005.5.390. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2005. PMID: 16417435
-
Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma phagocytophilum: Rickettsiales pathogens of veterinary and public health significance.Parasitol Res. 2015 Nov;114(11):3941-57. doi: 10.1007/s00436-015-4698-2. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Parasitol Res. 2015. PMID: 26346451 Review.
-
New records for Anaplasma phagocytophilum infection in small mammal species.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Mar 20;11(1):193. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2791-y. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29558990 Free PMC article.
-
Anaplasma phagocytophilum in small mammals and ticks in northeast Florida.J Vector Ecol. 2012 Jun;37(1):262-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1948-7134.2012.00226.x. J Vector Ecol. 2012. PMID: 22548563
-
[Ehrlichiosis and human anaplasmosis].Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2005 Jun-Jul;23(6):375-80. doi: 10.1157/13076178. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2005. PMID: 15970171 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Spatial and seasonal variation in the prevalence of Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in questing Ixodes ricinus ticks in Norway.Parasit Vectors. 2013 Jun 20;6:187. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-187. Parasit Vectors. 2013. PMID: 23786850 Free PMC article.
-
Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae infections in Ixodes ricinus ticks from urban and natural forested areas of Poland.Parasit Vectors. 2014 Mar 24;7:121. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-7-121. Parasit Vectors. 2014. PMID: 24661311 Free PMC article.
-
The dilution effect behind the scenes: testing the underlying assumptions of its mechanisms through quantifying the long-term dynamics and effects of a pathogen in multiple host species.Proc Biol Sci. 2021 Jun 9;288(1952):20210773. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2021.0773. Epub 2021 Jun 9. Proc Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34102894 Free PMC article.
-
Host-pathogen associations inferred from bloodmeal analyses of Ixodes scapularis ticks in a low biodiversity setting.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 Sep 18;90(9):e0066724. doi: 10.1128/aem.00667-24. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39207157
-
Vector competence of Ixodes ricinus instars for the transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in different small mammalian hosts.Parasit Vectors. 2024 Jan 18;17(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06110-7. Parasit Vectors. 2024. PMID: 38238796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Demma LJ, Holman RC, McQuiston JH, Krebs JW, Swerdlow DL. Epidemiology of human ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis in the United States, 2001–2002. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;73:400–9. - PubMed
-
- Foley JE, Foley P, Brown RN, Lane RS, Dumler JS, Madigan JE. Ecology of granulocytic ehrlichiosis and Lyme disease in the western United States. J Vector Ecol. 2004;29:41–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
