MicroRNAs reprogram normal fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer
- PMID: 23171795
- PMCID: PMC3685866
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0206
MicroRNAs reprogram normal fibroblasts into cancer-associated fibroblasts in ovarian cancer
Abstract
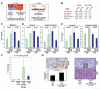
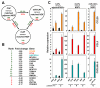
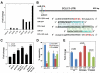
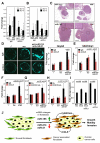
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) are a major constituent of the tumor stroma, but little is known about how cancer cells transform normal fibroblasts into CAFs. microRNAs (miRNA) are small noncoding RNA molecules that negatively regulate gene expression at a posttranscriptional level. Although it is clearly established that miRNAs are deregulated in human cancers, it is not known whether miRNA expression in resident fibroblasts is affected by their interaction with cancer cells. We found that in ovarian CAFs, miR-31 and miR-214 were downregulated, whereas miR-155 was upregulated when compared with normal or tumor-adjacent fibroblasts. Mimicking this deregulation by transfecting miRNAs and miRNA inhibitors induced a functional conversion of normal fibroblasts into CAFs, and the reverse experiment resulted in the reversion of CAFs into normal fibroblasts. The miRNA-reprogrammed normal fibroblasts and patient-derived CAFs shared a large number of upregulated genes highly enriched in chemokines, which are known to be important for CAF function. The most highly upregulated chemokine, CCL5, (C-C motif ligand 5) was found to be a direct target of miR-214. These results indicate that ovarian cancer cells reprogram fibroblasts to become CAFs through the action of miRNAs. Targeting these miRNAs in stromal cells could have therapeutic benefit.
Significance: The mechanism by which quiescent fibroblasts are converted into CAFs is unclear. The present study identifies a set of 3 miRNAs that reprogram normal fibroblasts to CAFs. These miRNAs may represent novel therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment.
©2012 AACR.
Figures
Comment in
-
MicroRNAs play a big role in regulating ovarian cancer-associated fibroblasts and the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Discov. 2012 Dec;2(12):1078-80. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0465. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 23230184 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Deregulated MicroRNAs in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts from Front Tumor Tissues of Lung Adenocarcinoma as Potential Predictors of Tumor Promotion.Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018 Oct;246(2):107-120. doi: 10.1620/tjem.246.107. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 30369556
-
MicroRNAs play a big role in regulating ovarian cancer-associated fibroblasts and the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Discov. 2012 Dec;2(12):1078-80. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0465. Cancer Discov. 2012. PMID: 23230184 Free PMC article.
-
[Dectection and analysis of miRNA expression in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014 Oct;30(10):1071-5. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25270211 Chinese.
-
Small role with big impact: miRNAs as communicators in the cross-talk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Feb 25;13(3):339-348. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.17680. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28367098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts.Mol Cancer. 2017 Aug 29;16(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0718-4. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28851377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Can Targeting Stroma Pave the Way to Enhanced Antitumor Immunity and Immunotherapy of Solid Tumors?Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Apr;4(4):269-78. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0011. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27036971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA modulators of epigenetic regulation, the tumor microenvironment and the immune system in lung cancer.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 7;14:34. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0302-8. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25743773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on anti-ovarian cancer mechanism of miRNA regulating tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1050917. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1050917. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melanoma miRNA trafficking controls tumour primary niche formation.Nat Cell Biol. 2016 Sep;18(9):1006-17. doi: 10.1038/ncb3399. Epub 2016 Aug 22. Nat Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27548915
-
Stromal miR-200s contribute to breast cancer cell invasion through CAF activation and ECM remodeling.Cell Death Differ. 2016 Jan;23(1):132-45. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.78. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Cell Death Differ. 2016. PMID: 26068592 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hanahan D, Coussens LM. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cell recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell. 2012;21:309–22. - PubMed
-
- Orimo A, Gupta P, Sgroi D, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, et al. Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis throught elevated SDF-1/CXCL 12 secretion. Cell. 2005;121:335–48. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

