Low vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 in cerebrospinal fluid of suicide attempters
- PMID: 23168996
- PMCID: PMC3565771
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2012.123
Low vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 in cerebrospinal fluid of suicide attempters
Abstract
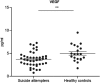
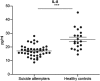
A dysregulated immune system influencing pathways for cytokine regulation and growth factor expression is implicated in the pathophysiology of several neuropsychiatric disorders. Here, we analyzed cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytokines and growth factors with an ultra-sensitive immunoassay system in 43 medication-free suicide attempters and 20 healthy male volunteers. CSF vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and CSF interleukin-8 (IL-8) levels were significantly lower in suicide attempters compared with healthy controls. Further, CSF VEGF showed a significant negative correlation with depression severity. CSF IL-6 levels did not differ between suicide attempters and healthy controls. Low CSF levels of VEGF may represent a lack of trophic support to neurons and downregulation of neurogenesis in the hippocampus reflecting more severe depressive states. IL-8 has also been reported as important in neuroprotection as well as having chemokine activity in the innate immune response. The results support a role for an impaired innate immunity and dysregulation of neuroprotection in the pathophysiology of depression and suicidal behavior.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-6 is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of suicide attempters and related to symptom severity.Biol Psychiatry. 2009 Aug 1;66(3):287-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2009.01.030. Epub 2009 Mar 6. Biol Psychiatry. 2009. PMID: 19268915
-
CSF 5-HIAA, cortisol and DHEAS levels in suicide attempters.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 Oct;23(10):1280-7. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.02.002. Epub 2013 Feb 28. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23453639
-
Low plasma vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with completed suicide.World J Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Sep;13(6):468-73. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2011.624549. Epub 2011 Nov 18. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22098148
-
The role of cytokines in the pathophysiology of suicidal behavior.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016 Jan;63:296-310. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.10.008. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016. PMID: 26546783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of inflammatory cytokines in physiopathology of suicidal behavior.J Affect Disord. 2015 Feb 1;172:219-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.09.057. Epub 2014 Oct 12. J Affect Disord. 2015. PMID: 25451421 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Neuronal VEGF Signaling in the Prefrontal Cortex in the Rapid Antidepressant Effects of Ketamine.Am J Psychiatry. 2019 May 1;176(5):388-400. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.17121368. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Am J Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30606046 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological modulation of HIF-1 in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023 Dec;130(12):1523-1535. doi: 10.1007/s00702-023-02698-3. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2023. PMID: 37740098 Review.
-
Association of interleukin-6 with suicidal ideation in veterans: a longitudinal perspective.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Sep 15;14:1231031. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1231031. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37779624 Free PMC article.
-
A Specific Inflammatory Profile Underlying Suicide Risk? Systematic Review of the Main Literature Findings.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 1;17(7):2393. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072393. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32244611 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral Markers of Suicidal Behavior: Current Findings and Clinical Implications.Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2023 Nov 30;21(4):650-664. doi: 10.9758/cpn.22.1046. Epub 2023 May 22. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37859438 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kim Y-K, Lee S-W, Kim S-H, Shim S-H, Han S-W, Choi S-H, et al. Differences in cytokines between non-suicidal patients and suicidal patients in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2008;32:356–361. - PubMed
-
- Lindqvist D, Janelidze S, Hagell P, Erhardt S, Samuelsson M, Minthon L, et al. Interleukin-6 is elevated in the cerebrospinal fluid of suicide attempters and related to symptom severity. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66:287–292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

