Transcriptional regulation of the Ufm1 conjugation system in response to disturbance of the endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and inhibition of vesicle trafficking
- PMID: 23152784
- PMCID: PMC3496721
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048587
Transcriptional regulation of the Ufm1 conjugation system in response to disturbance of the endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and inhibition of vesicle trafficking
Abstract
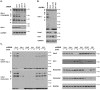
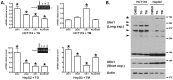
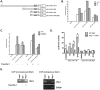
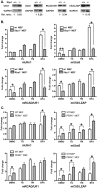
Homeostasis of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is essential for normal cellular functions. Disturbance of this homeostasis causes ER stress and activates the Unfolded Protein Response (UPR). The Ufm1 conjugation system is a novel Ubiquitin-like (Ubl) system whose physiological target(s) and biological functions remain largely undefined. Genetic study has demonstrated that the Ufm1-activating enzyme Uba5 is indispensible for erythroid differentiation in mice, highlighting the importance of this novel system in animal development. In this report we present the evidence for involvement of RCAD/Ufl1, a putative Ufm1-specific E3 ligase, and its binding partner C53/LZAP protein in ufmylation of endogenous Ufm1 targets. Moreover, we found that the Ufm1 system was transcriptionally up-regulated by disturbance of the ER homeostasis and inhibition of vesicle trafficking. Using luciferase reporter and ChIP assays, we dissected the Ufm1 promoter and found that Ufm1 was a potential target of Xbp-1, one of crucial transcription factors in UPR. We further examined the effect of Xbp-1 deficiency on the expression of the Ufm1 components. Interestingly, the expression of Ufm1, Uba5, RCAD/Ufl1 and C53/LZAP in wild-type mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) was significantly induced by inhibition of vesicle trafficking, but the induction was negated by Xbp-1 deficiency. Finally, we found that knockdown of the Ufm1 system in U2OS cells triggered UPR and amplification of the ER network. Taken together, our study provided critical insight into the regulatory mechanism of the Ufm1 system and established a direct link between this novel Ubl system and the ER network.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Emerging role of UFMylation in secretory cells involved in the endocrine system by maintaining ER proteostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 19;13:1085408. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1085408. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36743909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RCAD/Ufl1, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, is essential for hematopoietic stem cell function and murine hematopoiesis.Cell Death Differ. 2015 Dec;22(12):1922-34. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.51. Epub 2015 May 8. Cell Death Differ. 2015. PMID: 25952549 Free PMC article.
-
UFBP1, a Key Component of the Ufm1 Conjugation System, Is Essential for Ufmylation-Mediated Regulation of Erythroid Development.PLoS Genet. 2015 Nov 6;11(11):e1005643. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005643. eCollection 2015 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 26544067 Free PMC article.
-
Ufmylation bridges autophagy and ER homeostasis in plants.Autophagy. 2023 Oct;19(10):2830-2831. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2203985. Epub 2023 May 1. Autophagy. 2023. PMID: 37126567 Free PMC article.
-
Ufl1/RCAD, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, has an intricate connection with ER stress.Int J Biol Macromol. 2019 Aug 15;135:760-767. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.170. Epub 2019 May 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019. PMID: 31129212 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging role of UFMylation in secretory cells involved in the endocrine system by maintaining ER proteostasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 19;13:1085408. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1085408. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36743909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Migraine Genetic Variants Influence Cerebral Blood Flow.Headache. 2020 Jan;60(1):90-100. doi: 10.1111/head.13651. Epub 2019 Sep 26. Headache. 2020. PMID: 31559635 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of the UFM1 Toolkit for Profiling UFM1-Specific Proteases and Ligases.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Oct 22;57(43):14164-14168. doi: 10.1002/anie.201809232. Epub 2018 Oct 1. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 30188611 Free PMC article.
-
UFMylation of RPL26 links translocation-associated quality control to endoplasmic reticulum protein homeostasis.Cell Res. 2020 Jan;30(1):5-20. doi: 10.1038/s41422-019-0236-6. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 31595041 Free PMC article.
-
UFL1 Alleviates LPS-Induced Apoptosis by Regulating the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Bovine Ovarian Granulosa Cells.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 9;10(2):260. doi: 10.3390/biom10020260. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32050508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kaufman RJ (1999) Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev 13: 1211–1233. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Walter P (2007) Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 519–529. - PubMed
-
- Schroder M, Kaufman RJ (2005) The mammalian unfolded protein response. Annu Rev Biochem 74: 739–789. - PubMed
-
- Cox JS, Shamu CE, Walter P (1993) Transcriptional induction of genes encoding endoplasmic reticulum resident proteins requires a transmembrane protein kinase. Cell 73: 1197–1206. - PubMed
-
- Mori K, Ma W, Gething MJ, Sambrook J (1993) A transmembrane protein with a cdc2+/CDC28-related kinase activity is required for signaling from the ER to the nucleus. Cell 74: 743–756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

