Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88-ARNO-ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability
- PMID: 23143332
- PMCID: PMC3521847
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11603
Interleukin receptor activates a MYD88-ARNO-ARF6 cascade to disrupt vascular stability
Abstract
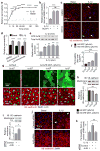
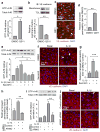
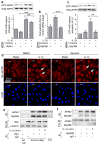
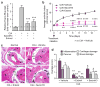
The innate immune response is essential for combating infectious disease. Macrophages and other cells respond to infection by releasing cytokines, such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), which in turn activate a well-described, myeloid-differentiation factor 88 (MYD88)-mediated, nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-dependent transcriptional pathway that results in inflammatory-cell activation and recruitment. Endothelial cells, which usually serve as a barrier to the movement of inflammatory cells out of the blood and into tissue, are also critical mediators of the inflammatory response. Paradoxically, the cytokines vital to a successful immune defence also have disruptive effects on endothelial cell-cell interactions and can trigger degradation of barrier function and dissociation of tissue architecture. The mechanism of this barrier dissolution and its relationship to the canonical NF-κB pathway remain poorly defined. Here we show that the direct, immediate and disruptive effects of IL-1β on endothelial stability in a human in vitro cell model are NF-κB independent and are instead the result of signalling through the small GTPase ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (ARF6) and its activator ARF nucleotide binding site opener (ARNO; also known as CYTH2). Moreover, we show that ARNO binds directly to the adaptor protein MYD88, and thus propose MYD88-ARNO-ARF6 as a proximal IL-1β signalling pathway distinct from that mediated by NF-κB. Finally, we show that SecinH3, an inhibitor of ARF guanine nucleotide-exchange factors such as ARNO, enhances vascular stability and significantly improves outcomes in animal models of inflammatory arthritis and acute inflammation.
Figures
Comment in
-
A new path to treating arthritis?Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013 Jan;9(1):2. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2012.209. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23183926 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Intra-endosomal pH-sensitive recruitment of the Arf-nucleotide exchange factor ARNO and Arf6 from cytoplasm to proximal tubule endosomes.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 25;276(21):18540-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M011577200. Epub 2001 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278939
-
Arf nucleotide binding site opener [ARNO] promotes sequential activation of Arf6, Cdc42 and Rac1 and insulin secretion in INS 832/13 β-cells and rat islets.Biochem Pharmacol. 2011 Apr 15;81(8):1016-27. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.01.006. Epub 2011 Jan 26. Biochem Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21276423 Free PMC article.
-
Shigella flexneri regulation of ARF6 activation during bacterial entry via an IpgD-mediated positive feedback loop.mBio. 2015 Mar 3;6(2):e02584. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02584-14. mBio. 2015. PMID: 25736891 Free PMC article.
-
ARNO is recruited by the neuronal adaptor FE65 to potentiate ARF6-mediated neurite outgrowth.Open Biol. 2022 Sep;12(9):220071. doi: 10.1098/rsob.220071. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Open Biol. 2022. PMID: 36168805 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MyD88: Therapeutic mechanisms and potential applications of the specific inhibitor ST2825.Inflamm Res. 2023 Nov;72(10-11):2023-2036. doi: 10.1007/s00011-023-01801-4. Epub 2023 Oct 9. Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37814128 Review.
Cited by
-
Two Hours of In Vivo Lung Perfusion Improves Lung Function in Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Spring;34(1):337-346. doi: 10.1053/j.semtcvs.2021.02.034. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 33713831 Free PMC article.
-
Thrombomodulin blocks calcineurin inhibitor-induced vascular permeability via inhibition of Src/VE-cadherin axis.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017 Feb;52(2):245-251. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2016.241. Epub 2016 Sep 19. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017. PMID: 27643869
-
Acridine orange leukocyte fluorography in mice.Exp Eye Res. 2014 Mar;120:15-9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Exp Eye Res. 2014. PMID: 24333760 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and the blood microvascular system.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014 Oct 23;7(1):a016345. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a016345. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2014. PMID: 25384307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GGA3 mediates TrkA endocytic recycling to promote sustained Akt phosphorylation and cell survival.Mol Biol Cell. 2015 Dec 1;26(24):4412-26. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-02-0087. Epub 2015 Oct 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26446845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Q, Verma IM. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2:725–734. - PubMed
-
- Collins T, et al. Transcriptional regulation of endothelial cell adhesion molecules: NF-kappa B and cytokine-inducible enhancers. FASEB J. 1995;9:899–909. - PubMed
-
- Liu SF, Malik AB. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006;290:L622–L645. - PubMed
-
- RothwARF DM, Karin M. The NF-kappa B activation pathway: a paradigm in information transfer from membrane to nucleus. Sci STKE. 1999:RE1. - PubMed
-
- Pober JS, Sessa WC. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nature reviews Immunology. 2007;7:803–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

