Transcriptome-wide miR-155 binding map reveals widespread noncanonical microRNA targeting
- PMID: 23142080
- PMCID: PMC3562697
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.002
Transcriptome-wide miR-155 binding map reveals widespread noncanonical microRNA targeting
Abstract
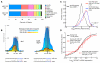
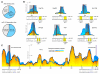
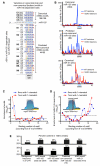
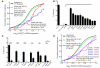
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are essential components of gene regulation, but identification of miRNA targets remains a major challenge. Most target prediction and discovery relies on perfect complementarity of the miRNA seed to the 3' untranslated region (UTR). However, it is unclear to what extent miRNAs target sites without seed matches. Here, we performed a transcriptome-wide identification of the endogenous targets of a single miRNA-miR-155-in a genetically controlled manner. We found that approximately 40% of miR-155-dependent Argonaute binding occurs at sites without perfect seed matches. The majority of these noncanonical sites feature extensive complementarity to the miRNA seed with one mismatch. These noncanonical sites confer regulation of gene expression, albeit less potently than canonical sites. Thus, noncanonical miRNA binding sites are widespread, often contain seed-like motifs, and can regulate gene expression, generating a continuum of targeting and regulation.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Argonaute CLIP Defines a Deregulated miR-122-Bound Transcriptome that Correlates with Patient Survival in Human Liver Cancer.Mol Cell. 2017 Aug 3;67(3):400-410.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.06.025. Epub 2017 Jul 20. Mol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28735896 Free PMC article.
-
CLIP-based prediction of mammalian microRNA binding sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Aug;41(14):e138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt435. Epub 2013 May 22. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23703212 Free PMC article.
-
A biophysical miRNA-mRNA interaction model infers canonical and noncanonical targets.Nat Methods. 2013 Mar;10(3):253-5. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2341. Epub 2013 Jan 20. Nat Methods. 2013. PMID: 23334102
-
MicroRNA Target Recognition: Insights from Transcriptome-Wide Non-Canonical Interactions.Mol Cells. 2016 May 31;39(5):375-81. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.0013. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Mol Cells. 2016. PMID: 27117456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions--beyond repression of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Sep;15(9):599-612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3765. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25022902 Review.
Cited by
-
Functionally distinct roles for different miR-155 expression levels through contrasting effects on gene expression, in acute myeloid leukaemia.Leukemia. 2017 Apr;31(4):808-820. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.279. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 27740637
-
Ago-RIP-Seq identifies Polycomb repressive complex I member CBX7 as a major target of miR-375 in prostate cancer progression.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 13;7(37):59589-59603. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10729. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27449098 Free PMC article.
-
Stage-specific regulation of natural killer cell homeostasis and response against viral infection by microRNA-155.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Apr 23;110(17):6967-72. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1304410110. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23572582 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for Therapeutic Targeting of MicroRNAs in Human Immunological Diseases.J Immunol. 2015 Jun 1;194(11):5047-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1403146. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25980029 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGO CLIP Reveals an Activated Network for Acute Regulation of Brain Glutamate Homeostasis in Ischemic Stroke.Cell Rep. 2019 Jul 23;28(4):979-991.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.06.075. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31340158 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

