Repeat expansions in the C9ORF72 gene contribute to Alzheimer's disease in Caucasians
- PMID: 23107433
- PMCID: PMC3586789
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2012.10.003
Repeat expansions in the C9ORF72 gene contribute to Alzheimer's disease in Caucasians
Abstract
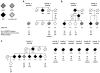
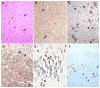
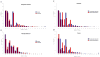
Recently, a hexanucleotide repeat expansion in the C9ORF72 gene has been identified to account for a significant portion of Caucasian families affected by frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Given the clinical overlap of FTD with Alzheimer's disease (AD), we hypothesized that C9ORF72 expansions might contribute to AD. In Caucasians, we found C9ORF72 expansions in the pathogenic range of FTD/ALS (>30 repeats) at a proportion of 0.76% in AD cases versus 0 in control subjects (p = 3.3E-03; 1182 cases, 1039 controls). In contrast, no large expansions were detected in individuals of African American ethnicity (291 cases, 620 controls). However, in the range of normal variation of C9ORF72 expansions (0-23 repeat copies), we detected significant differences in distribution and mean repeat counts between Caucasians and African Americans. Clinical and pathological re-evaluation of identified C9ORF72 expansion carriers revealed 9 clinical and/or autopsy confirmed AD and 2 FTD final diagnoses. Thus, our results support the notion that large C9ORF72 expansions lead to a phenotypic spectrum of neurodegenerative disease including AD.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no potential conflicts of interests related to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of C9orf72 repeat expansions in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia in mainland China.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Apr;35(4):936.e19-22. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2014. PMID: 24269022
-
Frontotemporal dementia with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a clinical comparison of patients with and without repeat expansions in C9orf72.Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2013 Apr;14(3):172-6. doi: 10.3109/21678421.2013.765485. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener. 2013. PMID: 23421625
-
Phenotypic variability and neuropsychological findings associated with C9orf72 repeat expansions in a Bulgarian dementia cohort.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 14;13(12):e0208383. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208383. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30550541 Free PMC article.
-
How do C9ORF72 repeat expansions cause amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia: can we learn from other noncoding repeat expansion disorders?Curr Opin Neurol. 2012 Dec;25(6):689-700. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0b013e32835a3efb. Curr Opin Neurol. 2012. PMID: 23160421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegeneration Related to C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion.Behav Neurol. 2019 Jan 15;2019:2909168. doi: 10.1155/2019/2909168. eCollection 2019. Behav Neurol. 2019. PMID: 30774737 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrant RNA homeostasis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: potential for new therapeutic targets?Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2014;4(6):417-37. doi: 10.2217/nmt.14.36. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2014. PMID: 25531686 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of CHCHD10 Mutation in Chinese Patients with Alzheimer Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Sep;54(7):5243-5247. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0056-3. Epub 2016 Aug 30. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27578015
-
C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat allele tagging SNPs: Associations with ALS risk and longevity.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 1;14:1087098. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1087098. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36936421 Free PMC article.
-
In-depth clinico-pathological examination of RNA foci in a large cohort of C9ORF72 expansion carriers.Acta Neuropathol. 2017 Aug;134(2):255-269. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1725-7. Epub 2017 May 15. Acta Neuropathol. 2017. PMID: 28508101 Free PMC article.
-
Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion in C9ORF72 Is Not Detected in the Treatment-Resistant Schizophrenia Patients of Chinese Han.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 21;10(12):e0145347. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145347. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26691640 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boeve BF, Boylan KB, Graff-Radford NR, DeJesus-Hernandez M, Knopman DS, Pedraza O, Vemuri P, Jones D, Lowe V, Murray ME, Dickson DW, Josephs KA, Rush BK, Machulda MM, Fields JA, Ferman TJ, Baker M, Rutherford NJ, Adamson J, Wszolek ZK, Adeli A, Savica R, Boot B, Kuntz KM, Gavrilova R, Reeves A, Whitwell J, Kantarci K, Jack CR, Jr, Parisi JE, Lucas JA, Petersen RC, Rademakers R. Characterization of frontotemporal dementia and/or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with the GGGGCC repeat expansion in C9ORF72. Brain: a journal of neurology. 2012;135(Pt 3):765–83. doi: 10.1093/brain/aws004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chio A, Borghero G, Restagno G, Mora G, Drepper C, Traynor BJ, Sendtner M, Brunetti M, Ossola I, Calvo A, Pugliatti M, Sotgiu MA, Murru MR, Marrosu MG, Marrosu F, Marinou K, Mandrioli J, Sola P, Caponnetto C, Mancardi G, Mandich P, La Bella V, Spataro R, Conte A, Monsurro MR, Tedeschi G, Pisano F, Bartolomei I, Salvi F, Lauria Pinter G, Simone I, Logroscino G, Gambardella A, Quattrone A, Lunetta C, Volanti P, Zollino M, Penco S, Battistini S, Renton AE, Majounie E, Abramzon Y, Conforti FL, Giannini F, Corbo M, Sabatelli M consortium I. Clinical characteristics of patients with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis carrying the pathogenic GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeat expansion of C9ORF72. Brain: a journal of neurology. 2012;135(Pt 3):784–93. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr366. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cooper-Knock J, Hewitt C, Highley JR, Brockington A, Milano A, Man S, Martindale J, Hartley J, Walsh T, Gelsthorpe C, Baxter L, Forster G, Fox M, Bury J, Mok K, McDermott CJ, Traynor BJ, Kirby J, Wharton SB, Ince PG, Hardy J, Shaw PJ. Clinico-pathological features in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with expansions in C9ORF72. Brain: a journal of neurology. 2012;135(Pt 3):751–64. doi: 10.1093/brain/awr365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science (New York, NY) 1993;261(5123):921–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

