Sequestration of G3BP coupled with efficient translation inhibits stress granules in Semliki Forest virus infection
- PMID: 23087212
- PMCID: PMC3521679
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-08-0619
Sequestration of G3BP coupled with efficient translation inhibits stress granules in Semliki Forest virus infection
Abstract
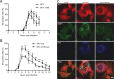
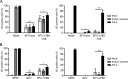
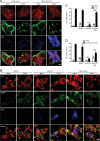
Dynamic, mRNA-containing stress granules (SGs) form in the cytoplasm of cells under environmental stresses, including viral infection. Many viruses appear to employ mechanisms to disrupt the formation of SGs on their mRNAs, suggesting that they represent a cellular defense against infection. Here, we report that early in Semliki Forest virus infection, the C-terminal domain of the viral nonstructural protein 3 (nsP3) forms a complex with Ras-GAP SH3-domain-binding protein (G3BP) and sequesters it into viral RNA replication complexes in a manner that inhibits the formation of SGs on viral mRNAs. A viral mutant carrying a C-terminal truncation of nsP3 induces more persistent SGs and is attenuated for propagation in cell culture. Of importance, we also show that the efficient translation of viral mRNAs containing a translation enhancer sequence also contributes to the disassembly of SGs in infected cells. Furthermore, we show that the nsP3/G3BP interaction also blocks SGs induced by other stresses than virus infection. This is one of few described viral mechanisms for SG disruption and underlines the role of SGs in antiviral defense.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Separate domains of G3BP promote efficient clustering of alphavirus replication complexes and recruitment of the translation initiation machinery.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Jun 14;15(6):e1007842. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007842. eCollection 2019 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31199850 Free PMC article.
-
Getah virus Nsp3 binds G3BP to block formation of bona fide stress granules.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Nov;279(Pt 2):135274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135274. Epub 2024 Sep 1. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39226976
-
Newcastle disease virus induces stable formation of bona fide stress granules to facilitate viral replication through manipulating host protein translation.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1337-1353. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600980R. Epub 2016 Dec 23. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28011649
-
Research Progress on the Structure and Function of G3BP.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 30;12:718548. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.718548. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34526993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rasputin a decade on and more promiscuous than ever? A review of G3BPs.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Mar;1866(3):360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30595162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of a non-canonical G3BP-binding sequence in a Mayaro virus nsP3 hypervariable domain.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 11;12:958176. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.958176. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36034716 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear proteins hijacked by mammalian cytoplasmic plus strand RNA viruses.Virology. 2015 May;479-480:457-74. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.03.001. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Virology. 2015. PMID: 25818028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypervariable domain of nonstructural protein nsP3 of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus determines cell-specific mode of virus replication.J Virol. 2013 Jul;87(13):7569-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00720-13. Epub 2013 May 1. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23637407 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of motif-mediated viral mimicry through the integration of host-pathogen interactions.Arch Microbiol. 2024 Feb 9;206(3):94. doi: 10.1007/s00203-024-03832-9. Arch Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38334822 Free PMC article.
-
The Viral Macrodomain Counters Host Antiviral ADP-Ribosylation.Viruses. 2020 Mar 31;12(4):384. doi: 10.3390/v12040384. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32244383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules. Curr Biol. 2009;19:R397–R398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

