Intracisternal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist prevents postoperative cognitive decline and neuroinflammatory response in aged rats
- PMID: 23077050
- PMCID: PMC3492959
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2173-12.2012
Intracisternal interleukin-1 receptor antagonist prevents postoperative cognitive decline and neuroinflammatory response in aged rats
Abstract
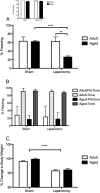
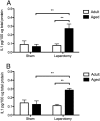
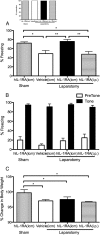
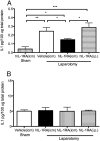
To investigate the role of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) in aged rats, we used laparotomy to mimic human abdominal surgery in adult (3 months) and aged (24 months) F344/BN rats. We demonstrated that memory consolidation of the hippocampal-dependent contextual fear-conditioning task is significantly impaired in aged but not young rats 4 d after surgery. Hippocampal-independent auditory-cued fear memory was not disrupted by laparotomy in either age group. The hippocampal-dependent memory impairment was paralleled by elevations of IL-1β in the hippocampus of aged animals 1 and 4 d after surgery. These findings support our substantial line of previous research showing that aged animals are more vulnerable to cognitive decline after a peripheral immune challenge. In addition, we demonstrated that a single intracisternal administration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA; 112 μg) at the time of surgery was sufficient to block both the behavioral deficit and the neuroinflammatory response. Injecting the same dose of IL-1RA peripherally failed to have a protective effect. These data provide strong support for the specific role of central, not peripheral, IL-1β in POCD. Furthermore, the long-lasting presence of IL-1RA in the brain (4 d) compared with in the blood (<24 h) underscores the value of intracisternal administration of IL-1RA for therapeutic purposes.
Figures
Comment in
-
Experimental insights into age-exacerbated cognitive dysfunction after peripheral surgery.Aging Cell. 2013 Jun;12(3):523-4. doi: 10.1111/acel.12066. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Aging Cell. 2013. PMID: 23461580
Similar articles
-
Experimental insights into age-exacerbated cognitive dysfunction after peripheral surgery.Aging Cell. 2013 Jun;12(3):523-4. doi: 10.1111/acel.12066. Epub 2013 Apr 2. Aging Cell. 2013. PMID: 23461580
-
IL-1RA blocks E. coli-induced suppression of Arc and long-term memory in aged F344xBN F1 rats.Brain Behav Immun. 2010 Feb;24(2):254-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2009.10.005. Epub 2009 Oct 12. Brain Behav Immun. 2010. PMID: 19822205 Free PMC article.
-
Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive dysfunction.Ann Neurol. 2010 Sep;68(3):360-8. doi: 10.1002/ana.22082. Ann Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20818791 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting tumor necrosis factor-α signaling attenuates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Aug;12(2):3095-100. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3744. Epub 2015 May 7. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25955232
-
High-fat diet consumption disrupts memory and primes elevations in hippocampal IL-1β, an effect that can be prevented with dietary reversal or IL-1 receptor antagonism.Brain Behav Immun. 2014 Nov;42:22-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2014.06.017. Epub 2014 Jul 3. Brain Behav Immun. 2014. PMID: 24998196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Microglia and modifiable life factors: Potential contributions to cognitive resilience in aging.Behav Brain Res. 2021 May 7;405:113207. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113207. Epub 2021 Feb 25. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33640394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evidence for a dysregulated immune system in the etiology of psychiatric disorders.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;8(4):900-20. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9462-8. Epub 2013 May 5. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23645137 Review.
-
The Role of Inflammation after Surgery for Elders (RISE) study: Examination of [11C]PBR28 binding and exploration of its link to post-operative delirium.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;27:102346. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102346. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32712451 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanins control neuroinflammation and consequent memory dysfunction in mice exposed to lipopolysaccharide.Mol Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;54(5):3350-3367. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-9900-8. Epub 2016 May 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 27167130
-
Surgery-Induced Hippocampal Angiotensin II Elevation Causes Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption via MMP/TIMP in Aged Rats.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Apr 26;10:105. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00105. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27199659 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abildstrom H, Rasmussen LS, Rentowl P, Hanning CD, Rasmussen H, Kristensen PA, Moller JT. Cognitive dysfunction 1–2 years after non-cardiac surgery in the elderly. ISPOCD Group. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2000;44:1246–1251. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Sprunger DB, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Memory for context is impaired by a post context exposure injection of interleukin-1 beta into dorsal hippocampus. Behav Brain Res. 2002;134:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Barrientos RM, Higgins EA, Biedenkapp JC, Sprunger DB, Wright-Hardesty KJ, Watkins LR, Rudy JW, Maier SF. Peripheral infection and aging interact to impair hippocampal memory consolidation. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27:723–732. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
