Absence of glial α-dystrobrevin causes abnormalities of the blood-brain barrier and progressive brain edema
- PMID: 23043099
- PMCID: PMC3510835
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.400044
Absence of glial α-dystrobrevin causes abnormalities of the blood-brain barrier and progressive brain edema
Abstract
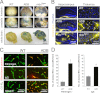
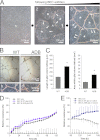
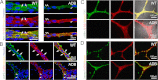
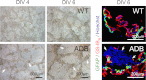
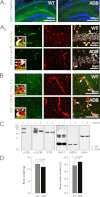
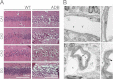
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays a key role in maintaining brain functionality. Although mammalian BBB is formed by endothelial cells, its function requires interactions between endotheliocytes and glia. To understand the molecular mechanisms involved in these interactions is currently a major challenge. We show here that α-dystrobrevin (α-DB), a protein contributing to dystrophin-associated protein scaffolds in astrocytic endfeet, is essential for the formation and functioning of BBB. The absence of α-DB in null brains resulted in abnormal brain capillary permeability, progressively escalating brain edema, and damage of the neurovascular unit. Analyses in situ and in two-dimensional and three-dimensional in vitro models of BBB containing α-DB-null astrocytes demonstrated these abnormalities to be associated with loss of aquaporin-4 water and Kir4.1 potassium channels from glial endfeet, formation of intracellular vacuoles in α-DB-null astrocytes, and defects of the astrocyte-endothelial interactions. These caused deregulation of tight junction proteins in the endothelia. Importantly, α-DB but not dystrophins showed continuous expression throughout development in BBB models. Thus, α-DB emerges as a central organizer of dystrophin-associated protein in glial endfeet and a rare example of a glial protein with a role in maintaining BBB function. Its abnormalities might therefore lead to BBB dysfunction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assembly of a perivascular astrocyte protein scaffold at the mammalian blood-brain barrier is dependent on alpha-syntrophin.Glia. 2006 Jun;53(8):879-90. doi: 10.1002/glia.20347. Glia. 2006. PMID: 16609960
-
Severe alterations of endothelial and glial cells in the blood-brain barrier of dystrophic mdx mice.Glia. 2003 May;42(3):235-51. doi: 10.1002/glia.10216. Glia. 2003. PMID: 12673830
-
Dystrophin-associated protein scaffolding in brain requires alpha-dystrobrevin.Neuroreport. 2010 Jul 14;21(10):695-9. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32833b0a3b. Neuroreport. 2010. PMID: 20508543 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocyte-endothelial interactions and blood-brain barrier permeability.J Anat. 2002 Jun;200(6):629-38. doi: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2002.00064.x. J Anat. 2002. PMID: 12162730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphofunctional aspects of the blood-brain barrier.Curr Drug Metab. 2012 Jan;13(1):50-60. doi: 10.2174/138920012798356970. Curr Drug Metab. 2012. PMID: 22292807 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Roles of Astrocyte-Derived Factors in Regulation of Blood-Brain Barrier Function after Brain Damage.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 29;20(3):571. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030571. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30699952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liprin-α-1 is a novel component of the murine neuromuscular junction and is involved in the organization of the postsynaptic machinery.Sci Rep. 2017 Aug 22;7(1):9116. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09590-7. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28831123 Free PMC article.
-
The neurovascular unit in leukodystrophies: towards solving the puzzle.Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022 Feb 28;19(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12987-022-00316-0. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2022. PMID: 35227276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glial influence on the blood brain barrier.Glia. 2013 Dec;61(12):1939-58. doi: 10.1002/glia.22575. Epub 2013 Oct 7. Glia. 2013. PMID: 24123158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Inflammation in Modulating Endogenous Hippocampal Neurogenesis After Spinal Cord Injury.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jun 18;15:682259. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.682259. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34220440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zlokovic B. V. (2008) The blood-brain barrier in health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron 57, 178–201 - PubMed
-
- Abbott N. J., Patabendige A. A., Dolman D. E., Yusof S. R., Begley D. J. (2010) Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 37, 13–25 - PubMed
-
- Giaume C., Koulakoff A., Roux L., Holcman D., Rouach N. (2010) Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 87–99 - PubMed
-
- Liebner S., Engelhardt B. (2005) in The Blood-Brain Barrier and Its Microenvironment: Basic Physiology to Neurological Disease (DeVries E., Prat A., eds) pp. 1–25, New York: Taylor & Francis
-
- Abbott N. J., Rönnbäck L., Hansson E., (2006) Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 41–53 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

