Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation
- PMID: 23032187
- PMCID: PMC3463848
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.241
Specific recognition of linear polyubiquitin by A20 zinc finger 7 is involved in NF-κB regulation
Abstract
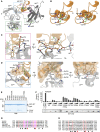
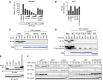
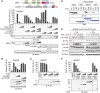
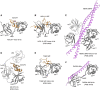
LUBAC (linear ubiquitin chain assembly complex) activates the canonical NF-κB pathway through linear polyubiquitination of NEMO (NF-κB essential modulator, also known as IKKγ) and RIP1. However, the regulatory mechanism of LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation remains elusive. Here, we show that A20 suppresses LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation by binding linear polyubiquitin via the C-terminal seventh zinc finger (ZF7), whereas CYLD suppresses it through deubiquitinase (DUB) activity. We determined the crystal structures of A20 ZF7 in complex with linear diubiquitin at 1.70-1.98 Å resolutions. The crystal structures revealed that A20 ZF7 simultaneously recognizes the Met1-linked proximal and distal ubiquitins, and that genetic mutations associated with B cell lymphomas map to the ubiquitin-binding sites. Our functional analysis indicated that the binding of A20 ZF7 to linear polyubiquitin contributes to the recruitment of A20 into a TNF receptor (TNFR) signalling complex containing LUBAC and IκB kinase (IKK), which results in NF-κB suppression. These findings provide new insight into the regulation of immune and inflammatory responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A20 inhibits LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation by binding linear polyubiquitin chains via its zinc finger 7.EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3845-55. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.240. Epub 2012 Aug 28. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 23032186 Free PMC article.
-
Recruitment of A20 by the C-terminal domain of NEMO suppresses NF-κB activation and autoinflammatory disease.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Feb 9;113(6):1612-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1518163113. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 26802121 Free PMC article.
-
Direct, noncatalytic mechanism of IKK inhibition by A20.Mol Cell. 2011 Nov 18;44(4):559-71. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.09.015. Mol Cell. 2011. PMID: 22099304 Free PMC article.
-
A20-mediated negative regulation of canonical NF-κB signaling pathway.Immunol Res. 2013 Dec;57(1-3):166-71. doi: 10.1007/s12026-013-8463-2. Immunol Res. 2013. PMID: 24242761 Review.
-
Regulation of NF-κB signaling by the A20 deubiquitinase.Cell Mol Immunol. 2012 Mar;9(2):123-30. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2011.59. Epub 2012 Feb 20. Cell Mol Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22343828 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Met1-linked ubiquitination in cell signaling regulation.Biophys Rep. 2024 Aug 31;10(4):230-240. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2024.230030. Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39281196 Free PMC article.
-
Linear ubiquitination signals in adaptive immune responses.Immunol Rev. 2015 Jul;266(1):222-36. doi: 10.1111/imr.12300. Immunol Rev. 2015. PMID: 26085218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell Death-Related Ubiquitin Modifications in Inflammatory Syndromes: From Mice to Men.Biomedicines. 2022 Jun 17;10(6):1436. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061436. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct phylogenetic relationships and biochemical properties of Arabidopsis ovarian tumor-related deubiquitinases support their functional differentiation.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 12;5:84. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00084. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24659992 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial signals, MyD88, and lymphotoxin drive TNF-independent intestinal epithelial tissue damage.J Clin Invest. 2022 Mar 1;132(5):e154993. doi: 10.1172/JCI154993. J Clin Invest. 2022. PMID: 35077396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams PD, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Hung LW, Ioerger TR, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Read RJ, Sacchettini JC, Sauter NK, Terwilliger TC (2002) PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 58: 1948–1954 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Neriah Y, Karin M (2011) Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-κB as the matchmaker. Nat Immunol 12: 715–723 - PubMed
-
- Bosanac I, Wertz IE, Pan B, Yu C, Kusam S, Lam C, Phu L, Phung Q, Maurer B, Arnott D, Kirkpatrick DS, Dixit VM, Hymowitz SG (2010) Ubiquitin binding to A20 ZnF4 is required for modulation of NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell 40: 548–557 - PubMed
-
- Brummelkamp TR, Nijman SM, Dirac AM, Bernards R (2003) Loss of the cylindromatosis tumour suppressor inhibits apoptosis by activating NF-κB. Nature 424: 797–801 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

