MicroRNA expression profiles of whole blood in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 23029380
- PMCID: PMC3460960
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046045
MicroRNA expression profiles of whole blood in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
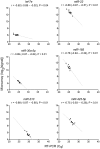
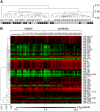
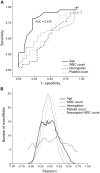
The association of lung cancer with changes in microRNAs in plasma shown in multiple studies suggests a utility for circulating microRNA biomarkers in non-invasive detection of the disease. We examined if presence of lung cancer is reflected in whole blood microRNA expression as well, possibly because of a systemic response. Locked nucleic acid microarrays were used to quantify the global expression of microRNAs in whole blood of 22 patients with lung adenocarcinoma and 23 controls, ten of whom had a radiographically detected non-cancerous lung nodule and the other 13 were at high risk for developing lung cancer because of a smoking history of >20 pack-years. Cases and controls differed significantly for age with a mean difference of 10.7 years, but not for gender, race, smoking history, blood hemoglobin, platelet count, or white blood cell count. Of 1282 quantified human microRNAs, 395 (31%) were identified as expressed in the study's subjects, with 96 (24%) differentially expressed between cases and controls. Classification analyses of microRNA expression data were performed using linear kernel support vector machines (SVM) and top-scoring pairs (TSP) methods, and classifiers to identify presence of lung adenocarcinoma were internally cross-validated. In leave-one-out cross-validation, the TSP classifiers had sensitivity and specificity of 91% and 100%, respectively. The values with SVM were both 91%. In a Monte Carlo cross-validation, average sensitivity and specificity values were 86% and 97%, respectively, with TSP, and 88% and 89%, respectively, with SVM. MicroRNAs miR-190b, miR-630, miR-942, and miR-1284 were the most frequent constituents of the classifiers generated during the analyses. These results suggest that whole blood microRNA expression profiles can be used to distinguish lung cancer cases from clinically relevant controls. Further studies are needed to validate this observation, including in non-adenocarcinomatous lung cancers, and to clarify upon the confounding effect of age.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Whole blood microRNA expression may not be useful for screening non-small cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2017 Jul 25;12(7):e0181926. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181926. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28742859 Free PMC article.
-
miR-1254 and miR-574-5p: serum-based microRNA biomarkers for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2011 Mar;6(3):482-8. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318208c785. J Thorac Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21258252
-
Circulating microRNA-339-5p and -21 in plasma as an early detection predictors of lung adenocarcinoma.Pathol Res Pract. 2018 Jan;214(1):119-125. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.10.011. Epub 2017 Oct 13. Pathol Res Pract. 2018. PMID: 29103767
-
[Molecular-genetic markers in lung cancer diagnostics].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2011 Mar-Apr;45(2):203-17. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2011. PMID: 21634110 Review. Russian.
-
Identification of differentially expressed circulating serum microRNA for the diagnosis and prognosis of Indian non-small cell lung cancer patients.Curr Probl Cancer. 2020 Aug;44(4):100540. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2020.100540. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Curr Probl Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32007320 Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral blood miR-328 expression as a potential biomarker for the early diagnosis of NSCLC.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 May 16;14(5):10332-42. doi: 10.3390/ijms140510332. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23681013 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of Mir-144-ZFX pathway in growth regulation of non-small-cell lung cancer.PLoS One. 2013 Sep 16;8(9):e74175. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074175. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24066116 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of microRNA-190b plays a role for decreased IGF-1 that induces insulin resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 20;9(2):e89446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089446. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586785 Free PMC article.
-
Muscle-Enriched MicroRNAs Isolated from Whole Blood Are Regulated by Exercise and Are Potential Biomarkers of Cardiorespiratory Fitness.Front Genet. 2016 Nov 15;7:196. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00196. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27895662 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse Modeling Reveals miRNA Signatures for Diagnostics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0140155. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140155. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26466382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ost D, Fein A (2000) Evaluation and management of the solitary pulmonary nodule. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 162: 782–787. - PubMed
-
- MacMahon H, Austin JH, Gamsu G, Herold CJ, Jett JR, et al. (2005) Guidelines for management of small pulmonary nodules detected on CT scans: a statement from the Fleischner Society. Radiology 237: 395–400. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

