Specific silencing of the REST target genes in insulin-secreting cells uncovers their participation in beta cell survival
- PMID: 23029270
- PMCID: PMC3447792
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045844
Specific silencing of the REST target genes in insulin-secreting cells uncovers their participation in beta cell survival
Abstract
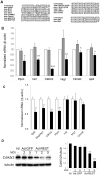
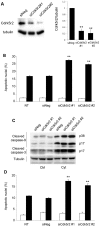
The absence of the transcriptional repressor RE-1 Silencing Transcription Factor (REST) in insulin-secreting beta cells is a major cue for the specific expression of a large number of genes. These REST target genes were largely ascribed to a function of neurotransmission in a neuronal context, whereas their role in pancreatic beta cells has been poorly explored. To identify their functional significance, we have generated transgenic mice expressing REST in beta cells (RIP-REST mice), and previously discovered that REST target genes are essential to insulin exocytosis. Herein we characterized a novel line of RIP-REST mice featuring diabetes. In diabetic RIP-REST mice, high levels of REST were associated with postnatal beta cell apoptosis, which resulted in gradual beta cell loss and sustained hyperglycemia in adults. Moreover, adenoviral REST transduction in INS-1E cells led to increased cell death under control conditions, and sensitized cells to death induced by cytokines. Screening for REST target genes identified several anti-apoptotic genes bearing the binding motif RE-1 that were downregulated upon REST expression in INS-1E cells, including Gjd2, Mapk8ip1, Irs2, Ptprn, and Cdk5r2. Decreased levels of Cdk5r2 in beta cells of RIP-REST mice further confirmed that it is controlled by REST, in vivo. Using siRNA-mediated knock-down in INS-1E cells, we showed that Cdk5r2 protects beta cells against cytokines and palmitate-induced apoptosis. Together, these data document that a set of REST target genes, including Cdk5r2, is important for beta cell survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional significance of repressor element 1 silencing transcription factor (REST) target genes in pancreatic beta cells.Diabetologia. 2008 Aug;51(8):1429-39. doi: 10.1007/s00125-008-0984-1. Epub 2008 Apr 3. Diabetologia. 2008. PMID: 18385973
-
SLC30A3 responds to glucose- and zinc variations in beta-cells and is critical for insulin production and in vivo glucose-metabolism during beta-cell stress.PLoS One. 2009 May 25;4(5):e5684. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0005684. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19492079 Free PMC article.
-
Pax6 is crucial for β-cell function, insulin biosynthesis, and glucose-induced insulin secretion.Mol Endocrinol. 2012 Apr;26(4):696-709. doi: 10.1210/me.2011-1256. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Mol Endocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22403172 Free PMC article.
-
Decompensation of β-cells in diabetes: when pancreatic β-cells are on ICE(R).J Diabetes Res. 2014;2014:768024. doi: 10.1155/2014/768024. Epub 2014 Feb 10. J Diabetes Res. 2014. PMID: 24672804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is 14-3-3 the Combination to Unlock New Pathways to Improve Metabolic Homeostasis and β-Cell Function?Diabetes. 2023 Aug 1;72(8):1045-1054. doi: 10.2337/db23-0094. Diabetes. 2023. PMID: 37471599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
REST is a major negative regulator of endocrine differentiation during pancreas organogenesis.Genes Dev. 2021 Sep 1;35(17-18):1229-1242. doi: 10.1101/gad.348501.121. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Genes Dev. 2021. PMID: 34385258 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of SF-1 transcription factor dosage impact on genome-wide binding and gene expression regulation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Oct;41(19):8896-907. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt658. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23907384 Free PMC article.
-
Scrt1, a transcriptional regulator of β-cell proliferation identified by differential chromatin accessibility during islet maturation.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 22;11(1):8800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88003-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33888791 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin43 Inhibition Prevents Human Vein Grafts Intimal Hyperplasia.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 23;10(9):e0138847. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0138847. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26398895 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic and Quantitative Proteomic Profiling Reveals Signaling Pathways Critical for Pancreatic Islet Maturation.Endocrinology. 2020 Dec 1;161(12):bqaa187. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa187. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 33053583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA, et al. (2003) Beta-cell deficit and increased beta-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52: 102–110. - PubMed
-
- Withers DJ, Burks DJ, Towery HH, Altamuro SL, Flint CL, et al. (1999) Irs-2 coordinates Igf-1 receptor-mediated beta-cell development and peripheral insulin signalling. Nat Genet 23: 32–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

