The potential economic value of a human norovirus vaccine for the United States
- PMID: 23026689
- PMCID: PMC3517973
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.09.040
The potential economic value of a human norovirus vaccine for the United States
Abstract
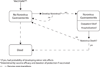
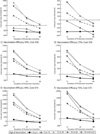
Vaccines against human norovirus are currently under development. We developed a simulation model to determine their potential economic value. Vaccination prevented 100-6125 norovirus gastroenteritis cases per 10,000 vaccinees. Low vaccine cost (≤$50) garnered cost-savings and a more expensive vaccine led to costs per case averted comparable to other vaccines. In the US, vaccination could avert approximately 1.0-2.2 million cases (efficacy 50%, 12 month duration), costing an additional $400 million to $1.0 billion, but could save ≤$2.1 billion (48 month duration). Human norovirus vaccination can offer economic value while averting clinical outcomes, depending on price, efficacy, and protection duration.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors are not aware of any significant conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cost-effectiveness of norovirus vaccination in children in Peru.Vaccine. 2015 Jun 17;33(27):3084-91. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.05.004. Epub 2015 May 15. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 25980428 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiologic challenges in norovirus vaccine development.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019;15(6):1279-1283. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2018.1553594. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2019. PMID: 30481104 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of immunity to norovirus gastroenteritis.Emerg Infect Dis. 2013 Aug;19(8):1260-7. doi: 10.3201/eid1908.130472. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23876612 Free PMC article.
-
The Vast and Varied Global Burden of Norovirus: Prospects for Prevention and Control.PLoS Med. 2016 Apr 26;13(4):e1001999. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001999. eCollection 2016 Apr. PLoS Med. 2016. PMID: 27115709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress toward norovirus vaccines: considerations for further development and implementation in potential target populations.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015;14(9):1241-53. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2015.1073110. Epub 2015 Jul 29. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2015. PMID: 26224658 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Norovirus Cultivation in Nontransformed Stem Cell-Derived Human Intestinal Enteroid Cultures: Success and Challenges.Viruses. 2019 Jul 11;11(7):638. doi: 10.3390/v11070638. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31336765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serological Correlates of Protection against a GII.4 Norovirus.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015 Aug;22(8):923-9. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00196-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26041041 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Norovirus: An Overview of Virology and Preventative Measures.Viruses. 2022 Dec 16;14(12):2811. doi: 10.3390/v14122811. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36560815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epidemiology of human noroviruses and updates on vaccine development.Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan;30(1):25-33. doi: 10.1097/MOG.0000000000000022. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24232370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Norovirus vaccines and potential antinorovirus drugs: recent advances and future perspectives.Future Virol. 2015;10(7):899-913. doi: 10.2217/fvl.15.57. Future Virol. 2015. PMID: 26568768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Phillips G, Tam CC, Conti S, Rodriguez LC, Brow D, Iturriza-Gomara M, et al. Community incidence of norovirus-associated infectious intestinal disease in England: improved estimates using viral load for norovirus diagnosis. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2010;171(9):1014–1022. - PubMed
-
- Patel MM, Hall AJ, Vinje J, Parashar UD. Noroviruses: a comprehensive review. J Clin Virol. 2009 Jan;44(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Hall AJ, Vinje J, Lopman B, Park GW, Yen C, Gregoricus N, et al. Updated norovirus outbreak management and disease prevention guidlines. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Reports: Recommendations and Reports. 2011;60(3) - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

