ORMDL3 is an inducible lung epithelial gene regulating metalloproteases, chemokines, OAS, and ATF6
- PMID: 23011799
- PMCID: PMC3478632
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1204151109
ORMDL3 is an inducible lung epithelial gene regulating metalloproteases, chemokines, OAS, and ATF6
Abstract
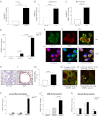
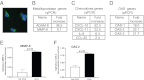
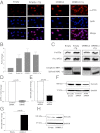
Orosomucoid like 3 (ORMDL3) has been strongly linked with asthma in genetic association studies, but its function in asthma is unknown. We demonstrate that in mice ORMDL3 is an allergen and cytokine (IL-4 or IL-13) inducible endoplasmic reticulum (ER) gene expressed predominantly in airway epithelial cells. Allergen challenge induces a 127-fold increase in ORMDL3 mRNA in bronchial epithelium in WT mice, with lesser 15-fold increases in ORMDL-2 and no changes in ORMDL-1. Studies of STAT-6-deficient mice demonstrated that ORMDL3 mRNA induction highly depends on STAT-6. Transfection of ORMDL3 in human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro induced expression of metalloproteases (MMP-9, ADAM-8), CC chemokines (CCL-20), CXC chemokines (IL-8, CXCL-10, CXCL-11), oligoadenylate synthetases (OAS) genes, and selectively activated activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), an unfolded protein response (UPR) pathway transcription factor. siRNA knockdown of ATF-6α in lung epithelial cells inhibited expression of SERCA2b, which has been implicated in airway remodeling in asthma. In addition, transfection of ORMDL3 in lung epithelial cells activated ATF6α and induced SERCA2b. These studies provide evidence of the inducible nature of ORMDL3 ER expression in particular in bronchial epithelial cells and suggest an ER UPR pathway through which ORMDL3 may be linked to asthma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ORMDL3 transgenic mice have increased airway remodeling and airway responsiveness characteristic of asthma.J Immunol. 2014 Apr 15;192(8):3475-87. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303047. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24623133 Free PMC article.
-
ORMDL3 Functions as a Negative Regulator of Antigen-Mediated Mast Cell Activation via an ATF6-UPR-Autophagy-Dependent Pathway.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 19;12:604974. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.604974. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679742 Free PMC article.
-
Rhinovirus Infection of ORMDL3 Transgenic Mice Is Associated with Reduced Rhinovirus Viral Load and Airway Inflammation.J Immunol. 2017 Oct 1;199(7):2215-2224. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601412. Epub 2017 Aug 21. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28827284 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome 17q21 Genes ORMDL3 and GSDMB in Asthma and Immune Diseases.Adv Immunol. 2017;135:1-52. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jul 19. Adv Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28826527 Review.
-
Sphingolipids, ORMDL3 and asthma: what is the evidence?Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017 Mar;20(2):99-103. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000349. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017. PMID: 28030368 Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Gasdermin B Gene GSDMB Polymorphisms with Risk of Allergic Diseases.Biochem Genet. 2021 Dec;59(6):1527-1543. doi: 10.1007/s10528-021-10073-8. Epub 2021 May 8. Biochem Genet. 2021. PMID: 33963941
-
The Association of GSDMB and ORMDL3 Gene Polymorphisms With Asthma: A Meta-Analysis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015 Mar;7(2):175-85. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.2.175. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2015. PMID: 25729625 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary ORMDL3 is critical for induction of Alternaria-induced allergic airways disease.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 May;139(5):1496-1507.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.033. Epub 2016 Sep 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27623174 Free PMC article.
-
The ORMDL3 Asthma Gene Regulates ICAM1 and Has Multiple Effects on Cellular Inflammation.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Feb 15;199(4):478-488. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201803-0438OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30339462 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophilia in severe asthma is reduced in Ormdl3 overexpressing mice.FASEB J. 2023 Mar;37(3):e22799. doi: 10.1096/fj.202201821R. FASEB J. 2023. PMID: 36753412 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

