Stromal cells expressing hedgehog-interacting protein regulate the proliferation of myeloid neoplasms
- PMID: 22961059
- PMCID: PMC3461706
- DOI: 10.1038/bcj.2012.36
Stromal cells expressing hedgehog-interacting protein regulate the proliferation of myeloid neoplasms
Abstract
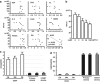
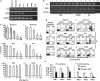
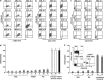
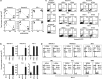
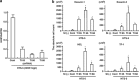
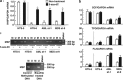
Aberrant reactivation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling has been described in a wide variety of human cancers including cancer stem cells. However, involvement of the Hh-signaling system in the bone marrow (BM) microenvironment during the development of myeloid neoplasms is unknown. In this study, we assessed the expression of Hh-related genes in primary human CD34(+) cells, CD34(+) blastic cells and BM stromal cells. Both Indian Hh (Ihh) and its signal transducer, smoothened (SMO), were expressed in CD34(+) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)-derived cells. However, Ihh expression was relatively low in BM stromal cells. Remarkably, expression of the intrinsic Hh-signaling inhibitor, human Hh-interacting protein (HHIP) in AML/MDS-derived stromal cells was markedly lower than in healthy donor-derived stromal cells. Moreover, HHIP expression levels in BM stromal cells highly correlated with their supporting activity for SMO(+) leukemic cells. Knockdown of HHIP gene in stromal cells increased their supporting activity although control cells marginally supported SMO(+) leukemic cell proliferation. The demethylating agent, 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine rescued HHIP expression via demethylation of HHIP gene and reduced the leukemic cell-supporting activity of AML/MDS-derived stromal cells. This indicates that suppression of stromal HHIP could be associated with the proliferation of AML/MDS cells.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Drug resistance is dramatically restored by hedgehog inhibitors in CD34+ leukemic cells.Cancer Sci. 2009 May;100(5):948-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01111.x. Epub 2009 Feb 24. Cancer Sci. 2009. PMID: 19245435 Free PMC article.
-
Nonhematopoietic cells represent a more rational target of in vivo hedgehog signaling affecting normal or acute myeloid leukemia progenitors.Exp Hematol. 2013 Oct;41(10):858-869.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2013.05.287. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Exp Hematol. 2013. PMID: 23747997
-
[Expression and Significance of Shh Signaling Pathway in Bone Marrow CD34+ Cells of Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Myelodysplasia-Related Changes].Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Oct;28(5):1637-1642. doi: 10.19746/j.cnki.issn.1009-2137.2020.05.034. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33067966 Chinese.
-
Hedgehog Signaling Links Chronic Inflammation to Gastric Cancer Precursor Lesions.Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Jan 16;3(2):201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2017.01.004. eCollection 2017 Mar. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28275687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hedgehog signaling in gastrointestinal carcinogenesis and the gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Mar;11(3):609-620. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2020.10.022. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33777671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A phase 2 trial of the oral smoothened inhibitor glasdegib in refractory myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS).Leuk Res. 2019 Jun;81:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2019.03.008. Epub 2019 Mar 30. Leuk Res. 2019. PMID: 31030089 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
miR-7977 inhibits the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway in bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.PLoS One. 2019 Mar 5;14(3):e0213220. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213220. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30835743 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog-Interacting Protein (HIP) Regulates Apoptosis Evasion and Angiogenic Function of Late Endothelial Progenitor Cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 29;7(1):12449. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12571-5. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28963460 Free PMC article.
-
Hedgehog/GLI signaling in hematopoietic development and acute myeloid leukemia-From bench to bedside.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 5;10:944760. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.944760. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35990601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phase I Study of LY2940680, a Smo Antagonist, in Patients with Advanced Cancer Including Treatment-Naïve and Previously Treated Basal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2018 May 1;24(9):2082-2091. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-0723. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29483143 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Deguchi K, Gilliland DG. Cooperativity between mutations in tyrosine kinases and in hematopoietic transcription factors in AML. Leukemia. 2002;16:740–744. - PubMed
-
- Yoshida K, Sanada M, Shiraishi Y, Nowak D, Nagata Y, Yamamoto R, et al. Frequent pathway mutations of splicing machinery in myelodysplasia. Nature. 2011;478:64–69. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

