The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression
- PMID: 22955988
- PMCID: PMC3431493
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.132159.111
The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression
Abstract
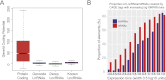
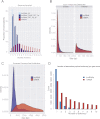
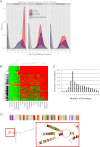
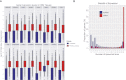
The human genome contains many thousands of long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). While several studies have demonstrated compelling biological and disease roles for individual examples, analytical and experimental approaches to investigate these genes have been hampered by the lack of comprehensive lncRNA annotation. Here, we present and analyze the most complete human lncRNA annotation to date, produced by the GENCODE consortium within the framework of the ENCODE project and comprising 9277 manually annotated genes producing 14,880 transcripts. Our analyses indicate that lncRNAs are generated through pathways similar to that of protein-coding genes, with similar histone-modification profiles, splicing signals, and exon/intron lengths. In contrast to protein-coding genes, however, lncRNAs display a striking bias toward two-exon transcripts, they are predominantly localized in the chromatin and nucleus, and a fraction appear to be preferentially processed into small RNAs. They are under stronger selective pressure than neutrally evolving sequences-particularly in their promoter regions, which display levels of selection comparable to protein-coding genes. Importantly, about one-third seem to have arisen within the primate lineage. Comprehensive analysis of their expression in multiple human organs and brain regions shows that lncRNAs are generally lower expressed than protein-coding genes, and display more tissue-specific expression patterns, with a large fraction of tissue-specific lncRNAs expressed in the brain. Expression correlation analysis indicates that lncRNAs show particularly striking positive correlation with the expression of antisense coding genes. This GENCODE annotation represents a valuable resource for future studies of lncRNAs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
GENCODE: the reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project.Genome Res. 2012 Sep;22(9):1760-74. doi: 10.1101/gr.135350.111. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22955987 Free PMC article.
-
Evolutionary annotation of conserved long non-coding RNAs in major mammalian species.Sci China Life Sci. 2015 Aug;58(8):787-98. doi: 10.1007/s11427-015-4881-9. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Sci China Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26117828
-
Long noncoding RNA repertoire in chicken liver and adipose tissue.Genet Sel Evol. 2017 Jan 10;49(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0275-0. Genet Sel Evol. 2017. PMID: 28073357 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNAs and tumorigenesis: genetic associations, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic strategies.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):163-75. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4445-4. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26586396 Review.
-
[Non-coding Natural Antisense RNA: Mechanisms of Action in the Regulation of Target Gene Expression and Its Clinical Implications].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020;140(5):687-700. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.20-00002. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2020. PMID: 32378673 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Transposable elements reveal a stem cell-specific class of long noncoding RNAs.Genome Biol. 2012 Nov 26;13(11):R107. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-11-r107. Genome Biol. 2012. PMID: 23181609 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in the Regulation of Cellular Immune Response and Inflammatory Diseases.Cells. 2022 Nov 17;11(22):3642. doi: 10.3390/cells11223642. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429069 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Phenotypes and Specific Transcription Patterns in Twenty Mouse Lines with Ablated LincRNAs.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0125522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125522. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909911 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of lncRNAs and mRNAs in intestinal macrophages.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Nov;22(5):3735-3746. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11470. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32901859 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Natural Antisense Transcripts in Mouse Brain and Their Association With Autism Spectrum Disorder Risk Genes.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Feb 25;14:624881. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.624881. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215: 403–410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
