Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) but not HIF-2 is essential for hypoxic induction of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases in primary newborn mouse epiphyseal growth plate chondrocytes
- PMID: 22930750
- PMCID: PMC3481313
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.352872
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) but not HIF-2 is essential for hypoxic induction of collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases in primary newborn mouse epiphyseal growth plate chondrocytes
Abstract
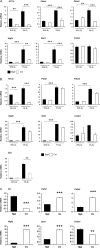
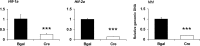
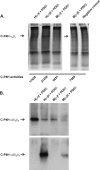
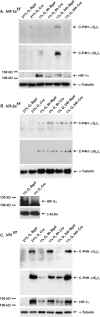
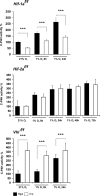
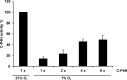
Hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) are the master regulators of hypoxia-responsive genes. They play a critical role in the survival, development, and differentiation of chondrocytes in the avascular hypoxic fetal growth plate, which is rich in extracellular matrix (ECM) and in its main component, collagens. Several genes involved in the synthesis, maintenance, and degradation of ECM are regulated by HIFs. Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylases (C-P4Hs) are key enzymes in collagen synthesis because the resulting 4-hydroxyprolines are necessary for the stability of all collagen molecules. The vertebrate C-P4Hs are α(2)β(2) tetramers with three isoforms of the catalytic α subunit, yielding C-P4Hs of types I-III. C-P4H-I is the main form in most cells, but C-P4H-II is the major form in chondrocytes. We postulated here that post-translational modification of collagens, particularly 4-hydroxylation of proline residues, could be one of the modalities by which HIF regulates the adaptive responses of chondrocytes in fetal growth plates. To address this hypothesis, we used primary epiphyseal growth plate chondrocytes isolated from newborn mice with conditionally inactivated genes for HIF-1α, HIF-2α, or the von Hippel-Lindau protein. The data obtained showed that C-P4H α(I) and α(II) mRNA levels were increased in hypoxic chondrocytes in a manner dependent on HIF-1 but not on HIF-2. Furthermore, the increases in the C-P4H mRNA levels were associated with both increased amounts of the C-P4H tetramers and augmented C-P4H activity in hypoxia. The hypoxia inducibility of the C-P4H isoenzymes is thus likely to ensure sufficient C-P4H activity for collagen synthesis occurring in chondrocytes in a hypoxic environment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe Extracellular Matrix Abnormalities and Chondrodysplasia in Mice Lacking Collagen Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Isoenzyme II in Combination with a Reduced Amount of Isoenzyme I.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16964-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.662635. Epub 2015 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26001784 Free PMC article.
-
An endoplasmic reticulum transmembrane prolyl 4-hydroxylase is induced by hypoxia and acts on hypoxia-inducible factor alpha.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 19;282(42):30544-52. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M704988200. Epub 2007 Aug 27. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17726031
-
Prolyl 4-hydroxylases, key enzymes in the synthesis of collagens and regulation of the response to hypoxia, and their roles as treatment targets.Ann Med. 2008;40(6):402-17. doi: 10.1080/07853890801986594. Ann Med. 2008. PMID: 19160570 Review.
-
Regulation of gene expression by the hypoxia-inducible factors.Mol Interv. 2002 Jul;2(4):229-43. doi: 10.1124/mi.2.4.229. Mol Interv. 2002. PMID: 14993394 Review.
-
HIF prolyl 4-hydroxylases and their potential as drug targets.Curr Pharm Des. 2009;15(33):3878-85. doi: 10.2174/138161209789649457. Curr Pharm Des. 2009. PMID: 19671043 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe Extracellular Matrix Abnormalities and Chondrodysplasia in Mice Lacking Collagen Prolyl 4-Hydroxylase Isoenzyme II in Combination with a Reduced Amount of Isoenzyme I.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16964-78. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.662635. Epub 2015 May 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26001784 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy Resistance, Cancer Stem Cells and ECM in Cancer: The Matrix Reloaded.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Oct 21;12(10):3067. doi: 10.3390/cancers12103067. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33096662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Five miRNAs considered as molecular targets for predicting neuroglioma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jan;37(1):1051-9. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3898-9. Epub 2015 Aug 14. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26269115
-
Recent Developments in the Study of the Microenvironment of Cancer and Drug Delivery.Curr Drug Metab. 2022;23(13):1027-1053. doi: 10.2174/1389200224666230110145513. Curr Drug Metab. 2022. PMID: 36627789
-
P4HA2 contributes to cervical cancer progression via inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cancer. 2020 Feb 21;11(10):2788-2799. doi: 10.7150/jca.38401. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32226497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandel N. S., Simon M. C. (2008) Hypoxia-inducible factor: roles in development, physiology, and disease. Cell Death Differ. 15, 619–620 - PubMed
-
- Kaelin W. G., Jr., Ratcliffe P. J. (2008) Oxygen sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase pathway. Mol. Cell 30, 393–402 - PubMed
-
- Myllyharju J. (2009) HIF prolyl 4-hydroxylases and their potential as drug targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 15, 3878–3885 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

