Mig-6 plays a critical role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and bile acid synthesis
- PMID: 22912762
- PMCID: PMC3422237
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042915
Mig-6 plays a critical role in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and bile acid synthesis
Abstract
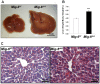
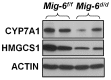
The disruption of cholesterol homeostasis leads to an increase in cholesterol levels which results in the development of cardiovascular disease. Mitogen Inducible Gene 6 (Mig-6) is an immediate early response gene that can be induced by various mitogens, stresses, and hormones. To identify the metabolic role of Mig-6 in the liver, we conditionally ablated Mig-6 in the liver using the Albumin-Cre mouse model (Alb(cre/+)Mig-6(f/f); Mig-6(d/d)). Mig-6(d/d) mice exhibit hepatomegaly and fatty liver. Serum levels of total, LDL, and HDL cholesterol and hepatic lipid were significantly increased in the Mig-6(d/d) mice. The daily excretion of fecal bile acids was significantly decreased in the Mig-6(d/d) mice. DNA microarray analysis of mRNA isolated from the livers of these mice showed alterations in genes that regulate lipid metabolism, bile acid, and cholesterol synthesis, while the expression of genes that regulate biliary excretion of bile acid and triglyceride synthesis showed no difference in the Mig-6(d/d) mice compared to Mig-6(f/f) controls. These results indicate that Mig-6 plays an important role in cholesterol homeostasis and bile acid synthesis. Mice with liver specific conditional ablation of Mig-6 develop hepatomegaly and increased intrahepatic lipid and provide a novel model system to investigate the genetic and molecular events involved in the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and bile acid synthesis. Defining the molecular mechanisms by which Mig-6 regulates cholesterol homeostasis will provide new insights into the development of more effective ways for the treatment and prevention of cardiovascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Amelioration of hypercholesterolemia by an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor in mice with liver-specific knockout of Mig-6.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 8;9(12):e114782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114782. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25486251 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Mig-6 in hepatic glucose metabolism.J Diabetes. 2016 Jan;8(1):86-97. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12261. Epub 2015 Mar 24. J Diabetes. 2016. PMID: 25594850
-
EP4 emerges as a novel regulator of bile acid synthesis and its activation protects against hypercholesterolemia.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018 Sep;1863(9):1029-1040. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2018. PMID: 29890224
-
Beyond cholesterol lowering: pleiotropic effects of bile acid binding resins against cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008 Oct;6(4):271-81. doi: 10.2174/157016108785909698. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18855715 Review.
-
Bile acid regulation of hepatic physiology: III. Regulation of bile acid synthesis: past progress and future challenges.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Apr;284(4):G551-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00468.2002. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12631556 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population.Hum Genomics. 2022 Apr 2;16(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s40246-022-00383-2. Hum Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35366956 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amelioration of hypercholesterolemia by an EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor in mice with liver-specific knockout of Mig-6.PLoS One. 2014 Dec 8;9(12):e114782. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114782. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25486251 Free PMC article.
-
ERRFI1 exacerbates hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury by promoting hepatocyte apoptosis and ferroptosis in a GRB2-dependent manner.Mol Med. 2024 Jun 11;30(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s10020-024-00837-4. Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38862918 Free PMC article.
-
Serum MIG6 concentration is increased by cholesterol-lowering treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypercholesterolemia.J Int Med Res. 2022 Mar;50(3):3000605221085079. doi: 10.1177/03000605221085079. J Int Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35301888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mig-6 gene knockout induces neointimal hyperplasia in the vascular smooth muscle cell.Dis Markers. 2014;2014:549054. doi: 10.1155/2014/549054. Epub 2014 Dec 10. Dis Markers. 2014. PMID: 25574067 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yusuf S, Hawken S, Ounpuu S, Dans T, Avezum A, et al. (2004) Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. Lancet 364: 937–952. - PubMed
-
- Executive Summary of The Third Report of The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, And Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol In Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III). JAMA 285: 2486–2497. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Daviglus ML, Garside DB, Dyer AR, Greenland P, et al. (2000) Relationship of baseline serum cholesterol levels in 3 large cohorts of younger men to long-term coronary, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality and to longevity. JAMA 284: 311–318. - PubMed
-
- Nabel EG (2003) Cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 349: 60–72. - PubMed
-
- Charlton-Menys V, Durrington PN (2008) Human cholesterol metabolism and therapeutic molecules. Exp Physiol 93: 27–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

