The proteasomal de-ubiquitinating enzyme POH1 promotes the double-strand DNA break response
- PMID: 22909820
- PMCID: PMC3463844
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2012.232
The proteasomal de-ubiquitinating enzyme POH1 promotes the double-strand DNA break response
Abstract
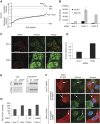
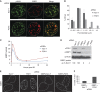
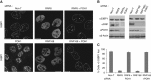
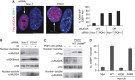
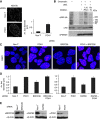
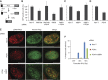
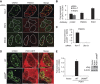
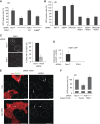
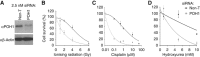
The regulation of Ubiquitin (Ub) conjugates generated by the complex network of proteins that promote the mammalian DNA double-strand break (DSB) response is not fully understood. We show here that the Ub protease POH1/rpn11/PSMD14 resident in the 19S proteasome regulatory particle is required for processing poly-Ub formed in the DSB response. Proteasome activity is required to restrict tudor domain-dependent 53BP1 accumulation at sites of DNA damage. This occurs both through antagonism of RNF8/RNF168-mediated lysine 63-linked poly-Ub and through the promotion of JMJD2A retention on chromatin. Consistent with this role POH1 acts in opposition to RNF8/RNF168 to modulate end-joining DNA repair. Additionally, POH1 acts independently of 53BP1 in homologous recombination repair to promote RAD51 loading. Accordingly, POH1-deficient cells are sensitive to DNA damaging agents. These data demonstrate that proteasomal POH1 is a key de-ubiquitinating enzyme that regulates ubiquitin conjugates generated in response to damage and that several aspects of the DSB response are regulated by the proteasome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
DNA damage response: restricting repair.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Oct;13(10):601. doi: 10.1038/nrm3437. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22948019 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
RNF8- and RNF168-dependent degradation of KDM4A/JMJD2A triggers 53BP1 recruitment to DNA damage sites.EMBO J. 2012 Apr 18;31(8):1865-78. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.47. Epub 2012 Feb 28. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22373579 Free PMC article.
-
RNF8 regulates assembly of RAD51 at DNA double-strand breaks in the absence of BRCA1 and 53BP1.Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 1;72(19):4974-83. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-1057. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22865450
-
Co-operation of BRCA1 and POH1 relieves the barriers posed by 53BP1 and RAP80 to resection.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Dec;41(22):10298-311. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt802. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 24013561 Free PMC article.
-
DNA DSB repair pathway choice: an orchestrated handover mechanism.Br J Radiol. 2014 Mar;87(1035):20130685. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130685. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24363387 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing roles of RNF8/RNF168 and deubiquitinating enzymes in ubiquitination-dependent DNA double-strand break response signaling and DNA-repair pathway choice.J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i33-i40. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw027. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26983989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitylation, neddylation and the DNA damage response.Open Biol. 2015 Apr;5(4):150018. doi: 10.1098/rsob.150018. Open Biol. 2015. PMID: 25833379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ubiquitylation-Mediated Fine-Tuning of DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 18;12(6):1617. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061617. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32570875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus infection disrupts homologous recombination in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing resection inhibitor ADRM1.J Clin Invest. 2023 Dec 1;133(23):e171533. doi: 10.1172/JCI171533. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37815873 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Basis for K63-Linked Ubiquitination Processes in Double-Strand DNA Break Repair: A Focus on Kinetics and Dynamics.J Mol Biol. 2017 Nov 10;429(22):3409-3429. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.05.029. Epub 2017 Jun 3. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28587922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ATM-mediated KDM2A phosphorylation is required for the DNA damage repair.Oncogene. 2016 Jan 21;35(3):301-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.81. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 25823024
References
-
- Acs K, Luijsterburg MS, Ackermann L, Salomons FA, Hoppe T, Dantuma NP (2011) The AAA-ATPase VCP/p97 promotes 53BP1 recruitment by removing L3MBTL1 from DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1345–1350 - PubMed
-
- Bekker-Jensen S, Rendtlew Danielsen J, Fugger K, Gromova I, Nerstedt A, Bartek J, Lukas J, Mailand N (2010) HERC2 coordinates ubiquitin-dependent assembly of DNA repair factors on damaged chromosomes. Nat Cell Biol 12: 80–86sup pp 1–12 - PubMed
-
- Berkovich E, Monnat RJ Jr, Kastan MB (2008) Assessment of protein dynamics and DNA repair following generation of DNA double-strand breaks at defined genomic sites. Nat Protoc 3: 915–922 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

