Myosin heavy chain kinases play essential roles in Ca2+, but not cAMP, chemotaxis and the natural aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum
- PMID: 22899719
- PMCID: PMC3517097
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.112474
Myosin heavy chain kinases play essential roles in Ca2+, but not cAMP, chemotaxis and the natural aggregation of Dictyostelium discoideum
Abstract
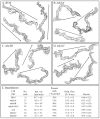
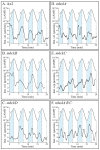
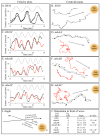
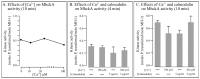
Behavioral analyses of the deletion mutants of the four known myosin II heavy chain (Mhc) kinases of Dictyostelium discoideum revealed that all play a minor role in the efficiency of basic cell motility, but none play a role in chemotaxis in a spatial gradient of cAMP generated in vitro. However, the two kinases MhckA and MhckC were essential for chemotaxis in a spatial gradient of Ca(2+), shear-induced directed movement, and reorientation in the front of waves of cAMP during natural aggregation. The phenotypes of the mutants mhckA(-) and mhckC(-) were highly similar to that of the Ca(2+) channel/receptor mutant iplA(-) and the myosin II phosphorylation mutant 3XALA, which produces constitutively unphosphorylated myosin II. These results demonstrate that IplA, MhckA and MhckC play a selective role in chemotaxis in a spatial gradient of Ca(2+), but not cAMP, and suggest that Ca(2+) chemotaxis plays a role in the orientation of cells in the front of cAMP waves during natural aggregation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The role of myosin heavy chain phosphorylation in Dictyostelium motility, chemotaxis and F-actin localization.J Cell Sci. 2004 Sep 15;117(Pt 20):4819-35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01358. Epub 2004 Aug 31. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15340009
-
RasC plays a role in transduction of temporal gradient information in the cyclic-AMP wave of Dictyostelium discoideum.Eukaryot Cell. 2004 Jun;3(3):646-62. doi: 10.1128/EC.3.3.646-662.2004. Eukaryot Cell. 2004. PMID: 15189986 Free PMC article.
-
The IplA Ca2+ channel of Dictyostelium discoideum is necessary for chemotaxis mediated through Ca2+, but not through cAMP, and has a fundamental role in natural aggregation.J Cell Sci. 2012 Apr 1;125(Pt 7):1770-83. doi: 10.1242/jcs.098301. Epub 2012 Feb 28. J Cell Sci. 2012. PMID: 22375061 Free PMC article.
-
A contextual framework for characterizing motility and chemotaxis mutants in Dictyostelium discoideum.J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002;23(7-8):659-72. doi: 10.1023/a:1024459124427. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 2002. PMID: 12952065 Review.
-
The regulation of myosin II in Dictyostelium.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep;85(9-10):969-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.04.004. Epub 2006 Jun 30. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16814425 Review.
Cited by
-
Mediated coalescence: a possible mechanism for tumor cellular heterogeneity.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Oct 15;5(11):3485-504. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26807328 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between phosphoinositide lipids and calcium signals at the leading edge of chemotaxing ameboid cells.Chem Phys Lipids. 2014 Sep;182:73-9. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 19. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014. PMID: 24451847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ion Signaling in Cell Motility and Development in Dictyostelium discoideum.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 10;14(7):830. doi: 10.3390/biom14070830. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of the Dictyostelium Myosin-II Heavy Chain Kinase A (MHCK-A) α-kinase domain apoenzyme reveals a novel autoinhibited conformation.Sci Rep. 2016 May 23;6:26634. doi: 10.1038/srep26634. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27211275 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN redundancy: overexpressing lpten, a homolog of Dictyostelium discoideum ptenA, the ortholog of human PTEN, rescues all behavioral defects of the mutant ptenA-.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 23;9(9):e108495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108495. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25247494 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Betapudi V., Shoebotham K., Egelhoff T. T. (2004). Genertion of double gene disruptons in Dictyostelium discoideum using a single antibiotic marker selection. Biotechniques 36, 106–112 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

