Activation of transcription factor MEF2D by bis(3)-cognitin protects dopaminergic neurons and ameliorates Parkinsonian motor defects
- PMID: 22891246
- PMCID: PMC3464532
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.367540
Activation of transcription factor MEF2D by bis(3)-cognitin protects dopaminergic neurons and ameliorates Parkinsonian motor defects
Abstract
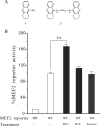
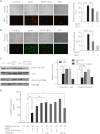
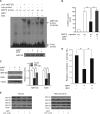
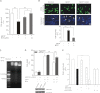
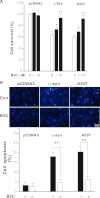
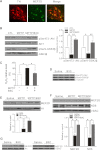
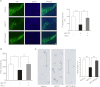
Parkinson disease (PD) is characterized by the selective demise of dopaminergic (DA) neurons in the substantial nigra pars compacta. Dysregulation of transcriptional factor myocyte enhancer factor 2D (MEF2D) has been implicated in the pathogenic process in in vivo and in vitro models of PD. Here, we identified a small molecule bis(3)-cognitin (B3C) as a potent activator of MEF2D. We showed that B3C attenuated the toxic effects of neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP(+)) by activating MEF2D via multiple mechanisms. B3C significantly reduced MPP(+)-induced oxidative stress and potentiated Akt to down-regulate the activity of MEF2 inhibitor glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β) in a DA neuronal cell line SN4741. Furthermore, B3C effectively rescued MEF2D from MPP(+)-induced decline in both nucleic and mitochondrial compartments. B3C offered SN4741 cells potent protection against MPP(+)-induced apoptosis via MEF2D. Interestingly, B3C also protected SN4741 cells from wild type or mutant A53T α-synuclein-induced cytotoxicity. Using the in vivo PD model of C57BL/6 mice treated with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride (MPTP), we showed that B3C maintained redox homeostasis, promoted Akt function activity, and restored MEF2D level in midbrain neurons. Moreover, B3C greatly prevented the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase signal in substantial nigra pars compacta DA neurons and ameliorated behavioral impairments in mice treated with MPTP. Collectedly, our studies identified B3C as a potent neuroprotective agent whose effectiveness relies on its ability to effectively up-regulate MEF2D in DA neurons against toxic stress in models of PD in vitro and in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Promising tacrine/huperzine A-based dimeric acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for neurodegenerative disorders: From relieving symptoms to modifying diseases through multitarget.J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(6):1381-1393. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15379. Epub 2021 Jul 5. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33930191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Substantial protection against MPTP-associated Parkinson's neurotoxicity in vitro and in vivo by anti-cancer agent SU4312 via activation of MEF2D and inhibition of MAO-B.Neuropharmacology. 2017 Nov;126:12-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.014. Epub 2017 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28807675
-
Salidroside protects dopaminergic neurons by regulating the mitochondrial MEF2D-ND6 pathway in the MPTP/MPP+ -induced model of Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2020 Apr;153(2):276-289. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14868. Epub 2019 Oct 27. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 31520529
-
Perturbation of transcription factor Nur77 expression mediated by myocyte enhancer factor 2D (MEF2D) regulates dopaminergic neuron loss in response to 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP).J Biol Chem. 2013 May 17;288(20):14362-14371. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.439216. Epub 2013 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23536182 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of myocyte enhancer factor-2 transcription factors by neurotoxins.Neurotoxicology. 2011 Oct;32(5):563-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2011.05.019. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Neurotoxicology. 2011. PMID: 21741404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Effects of Salidroside in the MPTP Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease: Involvement of the PI3K/Akt/GSK3β Pathway.Parkinsons Dis. 2016;2016:9450137. doi: 10.1155/2016/9450137. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Parkinsons Dis. 2016. PMID: 27738547 Free PMC article.
-
Potent Protection Against MPP+-Induced Neurotoxicity via Activating Transcription Factor MEF2D by a Novel Derivative of Naturally Occurring Danshensu/Tetramethylpyrazine.Neuromolecular Med. 2016 Dec;18(4):561-572. doi: 10.1007/s12017-016-8399-5. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Neuromolecular Med. 2016. PMID: 27277280
-
No synergism between bis(propyl)-cognitin and rasagiline on protecting dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson's disease mice.Neural Regen Res. 2016 Aug;11(8):1339-46. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.189201. Neural Regen Res. 2016. PMID: 27651784 Free PMC article.
-
Promising tacrine/huperzine A-based dimeric acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for neurodegenerative disorders: From relieving symptoms to modifying diseases through multitarget.J Neurochem. 2021 Sep;158(6):1381-1393. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15379. Epub 2021 Jul 5. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33930191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nato3 integrates with the Shh-Foxa2 transcriptional network regulating the differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.J Mol Neurosci. 2013 Sep;51(1):13-27. doi: 10.1007/s12031-012-9939-6. Epub 2012 Dec 21. J Mol Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23254923
References
-
- Tatton N. A., Kish S. J. (1997) In situ detection of apoptotic nuclei in the substantia nigra compacta of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated mice using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase labeling and acridine orange staining. Neuroscience 77, 1037–1048 - PubMed
-
- de Lau L. M., Breteler M. M. (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson disease. Lancet Neurol. 5, 525–535 - PubMed
-
- Wang L., Yang H. J., Xia Y. Y., Feng Z. W. (2010) Insulin-like growth factor 1 protects human neuroblastoma cells SH-EP1 against MPP+-induced apoptosis by AKT/GSK3β/JNK signaling. Apoptosis 15, 1470–1479 - PubMed
-
- Sun X., Huang L., Zhang M., Sun S., Wu Y. (2010) Insulin like growth factor-1 prevents 1-mentyl-4-phenylphyridinium-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells through activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β. Toxicology 271, 5–12 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

