Routine use of microbial whole genome sequencing in diagnostic and public health microbiology
- PMID: 22876174
- PMCID: PMC3410874
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002824
Routine use of microbial whole genome sequencing in diagnostic and public health microbiology
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and have the following conflicts: CUK, MJE, EJPC, NMB, MTGH, GD, SDB, JP, and SJP have collaborated with Illumina Ltd. on a number of scientific projects. JP has received funding for travel and accommodation from Pacific Biosciences Inc. and Illumina Inc. NMB is a consultant for Astellas Pharma Ltd. SHG has received payments from Bayer Schering Health Care for lectures. SJP is a consultant for Pfizer Inc. This does not alter our adherence to all
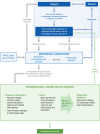
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rapid whole-genome sequencing of bacterial pathogens in the clinical microbiology laboratory--pipe dream or reality?J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Oct;67(10):2307-8. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks247. Epub 2012 Jun 22. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22729921 Review.
-
Genome sequencing in clinical microbiology.Nat Biotechnol. 2012 Nov;30(11):1068-71. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2410. Nat Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 23138305 No abstract available.
-
Application of 'next-generation' sequencing technologies to microbial genetics.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009 Apr;7(4):287-96. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2122. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19287448 Review.
-
Transforming clinical microbiology with bacterial genome sequencing.Nat Rev Genet. 2012 Sep;13(9):601-612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3226. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Nat Rev Genet. 2012. PMID: 22868263 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of genomic DNA sequences as type material for valid publication of bacterial species names will have severe implications for clinical microbiology and related disciplines.Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019 Sep;95(1):102-103. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 30981555 No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The healthy human microbiome.Genome Med. 2016 Apr 27;8(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0307-y. Genome Med. 2016. PMID: 27122046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequencing Mycobacteria and Algorithm-determined Resistant Tuberculosis Treatment (SMARTT): a study protocol for a phase IV pragmatic randomized controlled patient management strategy trial.Trials. 2022 Oct 8;23(1):864. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06793-w. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36209235 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of multidrug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates from Myanmar.J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2016 Sep;6:113-117. doi: 10.1016/j.jgar.2016.04.008. Epub 2016 May 30. J Glob Antimicrob Resist. 2016. PMID: 27530852 Free PMC article.
-
Detection, Characterization, and Typing of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli.Front Microbiol. 2016 Apr 12;7:478. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00478. eCollection 2016. Front Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 27148176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Incidence and characterisation of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from nasal colonisation in participants attending a cattle veterinary conference in the UK.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 15;8(7):e68463. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068463. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23869220 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Venter JC (2010) Multiple personal genomes await. Nature 464: 676–677. - PubMed
-
- Lander ES (2011) Initial impact of the sequencing of the human genome. Nature 470: 187–197. - PubMed
-
- Loman NJ, Pallen MJ (2008) XDR-TB genome sequencing: a glimpse of the microbiology of the future. Future Microbiol 3: 111–113. - PubMed
-
- Baldry S (2010) Attack of the clones. Nat Rev Microbiol 8: 390. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

