Upregulation of the E3 ligase NEDD4-1 by oxidative stress degrades IGF-1 receptor protein in neurodegeneration
- PMID: 22875931
- PMCID: PMC3681290
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1836-12.2012
Upregulation of the E3 ligase NEDD4-1 by oxidative stress degrades IGF-1 receptor protein in neurodegeneration
Abstract
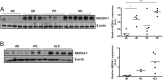
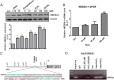
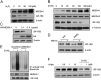
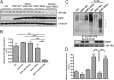
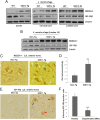
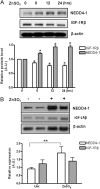
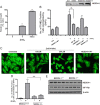
The importance of ubiquitin E3 ligases in neurodegeneration is being increasingly recognized. The crucial role of NEDD4-1 in neural development is well appreciated; however, its role in neurodegeneration remains unexplored. Herein, we report increased NEDD4-1 expression in the degenerated tissues of several major neurodegenerative diseases. Moreover, its expression is upregulated in cultured neurons in response to various neurotoxins, including zinc and hydrogen superoxide, via transcriptional activation likely mediated by the reactive oxygen species (ROS)-responsive FOXM1B. Reduced protein levels of the insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGF-1Rβ) were observed as a consequence of upregulated NEDD4-1 via the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Overexpression of a familial mutant form of superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) (G93A) in neuroblastoma cells resulted in a similar reduction of IGF-1Rβ protein. This inverse correlation between NEDD4-1 and IGF-1Rβ was also observed in the cortex and spinal cords of mutant (G93A) SOD1 transgenic mice at a presymptomatic age, which was similarly induced by in vivo-administered zinc in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Furthermore, histochemistry reveals markedly increased NEDD4-1 immunoreactivity in the degenerating/degenerated motor neurons in the lumbar anterior horn of the spinal cord, suggesting a direct causative role for NEDD4-1 in neurodegeneration. Indeed, downregulation of NEDD4-1 by shRNA or overexpression of a catalytically inactive form rescued neurons from zinc-induced cell death. Similarly, neurons with a NEDD4-1 haplotype are more resistant to apoptosis, largely due to expression of higher levels of IGF-1Rβ.Together, our work identifies a novel molecular mechanism for ROS-upregulated NEDD4-1 and the subsequently reduced IGF-1Rβ signaling in neurodegeneration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional interaction of phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) with the E3 ligase NEDD4-1 during neuronal response to zinc.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 26;285(13):9847-9857. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.091637. Epub 2010 Jan 25. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20100827 Free PMC article.
-
The Grb10/Nedd4 complex regulates ligand-induced ubiquitination and stability of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor.Mol Cell Biol. 2003 May;23(9):3363-72. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.9.3363-3372.2003. Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12697834 Free PMC article.
-
Grb10/Nedd4-mediated multiubiquitination of the insulin-like growth factor receptor regulates receptor internalization.J Cell Physiol. 2008 Aug;216(2):426-37. doi: 10.1002/jcp.21405. J Cell Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18286479
-
The Roles of NEDD4 Subfamily of HECT E3 Ubiquitin Ligases in Neurodevelopment and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3882. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073882. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nedd4 and Nedd4-2: ubiquitin ligases at work in the neuron.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Mar;45(3):706-10. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23262292 Review.
Cited by
-
A Fundamental Role for Oxidants and Intracellular Calcium Signals in Alzheimer's Pathogenesis-And How a Comprehensive Antioxidant Strategy May Aid Prevention of This Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 21;22(4):2140. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042140. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33669995 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting PY motif-mediated protein-protein interactions in the Nedd4 family of ubiquitin ligases.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 12;16(10):e0258315. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258315. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34637467 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Link between Alzheimer's Disease and Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity.Neural Plast. 2016;2016:7969272. doi: 10.1155/2016/7969272. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Neural Plast. 2016. PMID: 27019755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nedd4 haploinsufficient mice display moderate insulin resistance, enhanced lipolysis, and protection against high-fat diet-induced obesity.Endocrinology. 2015 Apr;156(4):1283-91. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1909. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25607895 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-like Proteins in Cancer, Neurodegenerative Disorders, and Heart Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 2;23(9):5053. doi: 10.3390/ijms23095053. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563444 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adem A, Ekblom J, Gillberg PG, Jossan SS, Höög A, Winblad B, Aquilonius SM, Wang LH, Sara V. Insulin-like growth factor-1 receptors in human spinal cord: changes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neural Transm Gen Sect. 1994;97:73–84. - PubMed
-
- Baker J, Liu JP, Robertson EJ, Efstratiadis A. Role of insulin-like growth factors in embryonic and postnatal growth. Cell. 1993;75:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Barber SC, Mead RJ, Shaw PJ. Oxidative stress in ALS: a mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1762:1051–1067. - PubMed
-
- Butler AA, Yakar S, Gewolb IH, Karas M, Okubo Y, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction: at the interface between physiology and cell biology. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 1998;121:19–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
