Antibodies against human BLyS and APRIL attenuate EAE development in marmoset monkeys
- PMID: 22870852
- PMCID: PMC3419352
- DOI: 10.1007/s11481-012-9384-x
Antibodies against human BLyS and APRIL attenuate EAE development in marmoset monkeys
Erratum in
- J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Mar;8(1):370. Oh, Luke [added]
Abstract
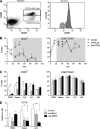
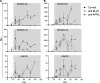
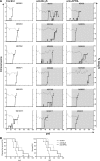
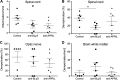
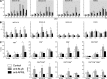
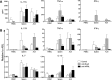
B lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS, also indicated as BAFF (B-cell activating factor) and CD257), and A Proliferation Inducing Ligand (APRIL, CD256) are two members of the TNF superfamily with a central role in B cell survival. Antibodies against these factors have potential therapeutic relevance in autoimmune inflammatory disorders with a proven pathogenic contribution of B cells, such as multiple sclerosis (MS). In the current study we performed a multi-parameter efficacy comparison of monoclonal antibodies against human anti-BLyS and anti-APRIL in a common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). A MS-like disease was induced by immunization with recombinant human myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (rhMOG) in complete Freund's adjuvant. The results show that the anti-BLyS and anti-APRIL antibody cause significant depletion of circulating CD20+ B cells, but a small subset of CD20 + CD40(high) B cells was not depleted. Induction of CD20+ B cell depletion from lymph nodes was only observed in the anti-BLyS treated monkeys. Both antibodies had a significant inhibitory effect on disease development, but all monkeys developed clinically evident EAE. Anti-BLyS treated monkeys were sacrificed with the same clinical signs as saline-treated monkeys, but nevertheless displayed significantly reduced spinal cord demyelination. This effect was not observed in the anti-APRIL treated monkeys. The two antibodies had a different effect on T cell subset activation and the profiles of ex vivo released cytokines. In conclusion, treatment with anti-BLyS and anti-APRIL delays the development of neurological disease in a relevant preclinical model of MS. The two mAbs achieve this effect via different mechanisms.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The different clinical effects of anti-BLyS, anti-APRIL and anti-CD20 antibodies point at a critical pathogenic role of γ-herpesvirus infected B cells in the marmoset EAE model.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013 Jun;8(3):727-38. doi: 10.1007/s11481-013-9448-6. Epub 2013 Mar 19. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23508625
-
Immune profile of an atypical EAE model in marmoset monkeys immunized with recombinant human myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in incomplete Freund's adjuvant.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Sep 17;12:169. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0378-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26377397 Free PMC article.
-
Late B cell depletion with a human anti-human CD20 IgG1κ monoclonal antibody halts the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in marmosets.J Immunol. 2010 Oct 1;185(7):3990-4003. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001393. Epub 2010 Aug 25. J Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20739677
-
Telitacicept as a BLyS/APRIL dual inhibitor for autoimmune disease.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021 Dec;43(6):666-673. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2021.1973493. Epub 2021 Sep 14. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021. PMID: 34519594 Review.
-
Targeting B-lymphocyte stimulator/B-cell activating factor and a proliferation-inducing ligand in hematologic malignancies.Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2006 Sep;7(2):106-8. doi: 10.3816/CLM.2006.n.046. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma. 2006. PMID: 17026820 Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple sclerosis and drug discovery: A work of translation.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jun;68:103392. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103392. Epub 2021 May 24. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34044219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Tolerogenic Role of Cathepsin G in a Primate Model of Multiple Sclerosis: Abrogation by Epstein-Barr Virus Infection.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2020 Jun 16;68(4):21. doi: 10.1007/s00005-020-00587-1. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2020. PMID: 32556812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Good efficacy achieved by telitacicept, corticosteroids and immunosuppressants in the treatment of SLE combined with MOG-AD.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2023 Oct 18;7(3):rkad088. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkad088. eCollection 2023. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2023. PMID: 37937177 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
An Evaluation of 20 Years of EU Framework Programme-Funded Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Translational Research in Non-Human Primates.Front Immunol. 2016 Nov 7;7:462. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00462. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27872622 Free PMC article.
-
B Cell in Autoimmune Diseases.Scientifica (Cairo). 2012;2012:215308. doi: 10.6064/2012/215308. Scientifica (Cairo). 2012. PMID: 23807906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boon L, Brok HP, Bauer J, Ortiz-Buijsse A, Schellekens MM, Ramdien-Murli S, Blezer E, van Meurs M, Ceuppens J, de Boer M, ’t Hart BA, Laman JD. Prevention of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the common marmoset (Callithrix jacchus) using a chimeric antagonist monoclonal antibody against human CD40 is associated with altered B cell responses. J Immunol. 2001;167:2942–2949. - PubMed
-
- Brok HP, Uccelli A, Kerlero De Rosbo N, Bontrop RE, Roccatagliata L, de Groot NG, Capello E, Laman JD, Nicolay K, Mancardi GL, Ben-Nun A, ’t Hart BA. Myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis in common marmosets: the encephalitogenic T cell epitope pMOG24-36 is presented by a monomorphic MHC class II molecule. J Immunol. 2000;165:1093–1101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

