Down-regulation of S100A11, a calcium-binding protein, in human endometrium may cause reproductive failure
- PMID: 22869607
- PMCID: PMC3462935
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-2075
Down-regulation of S100A11, a calcium-binding protein, in human endometrium may cause reproductive failure
Abstract
Background: Low expression levels of S100A11 proteins were demonstrated in the placental villous tissue of patients with early pregnancy loss, and S100A11 is a Ca2+-binding protein that interprets the calcium fluctuations and elicits various cellular responses.
Objectives: The objective of the study was to determine S100A11 expression in human endometrium and its roles in endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation.
Methods: S100A11 expression in human endometrium was analyzed using quantitative RT-PCR, Western blot, and immunohistochemical techniques. The effects of S100A11 on embryo implantation were examined using in vivo mouse model, and JAr (a human choriocarcinoma cell line) spheroid attachment assays. The effects of endometrial S100A11 on factors related to endometrial receptivity and immune responses were examined. Using a fluorescence method, we examined the changes in cytosolic Ca2+ and Ca2+ release from intracellular stores in epidermal growth factor (EGF)-treated endometrial cells transfected with or without S100A11 small interfering RNA.
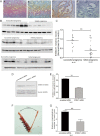
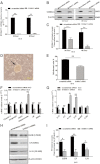
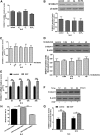
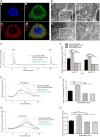
Results: S100A11 was expressed in human endometrium. S100A11 protein levels were significantly lower in endometrium of women with failed pregnancy than that in women with successful pregnancy outcomes. The knockdown of endometrial S100A11 not only reduced embryo implantation rate in mouse but also had adverse effects on the expression of factors related to endometrial receptivity and immune responses in human endometrial cells. Immunofluorescence analysis showed that S100A11 proteins were mainly localized in endoplasmic reticulum. The EGF up-regulated endometrial S100A11 expression and promoted the Ca2+ uptake and release from Ca2+ stores, which was inhibited by the knockdown of S100A11.
Conclusions: Endometrial S100A11 is a crucial intermediator in EGF-stimulated embryo adhesion, endometrium receptivity, and immunotolerance via affecting Ca2+ uptake and release from intracellular Ca2+ stores. Down-regulation of S100A11 may cause reproductive failure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Administration of calcitonin promotes blastocyst implantation in mice by up-regulating integrin β3 expression in endometrial epithelial cells.Hum Reprod. 2012 Dec;27(12):3540-51. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des330. Epub 2012 Sep 20. Hum Reprod. 2012. PMID: 23001774
-
Functional expression of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in human endometrium: a novel mechanism involved in endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Feb;97(2):543-53. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2108. Epub 2011 Dec 14. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22170720
-
PCAF impairs endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation by down-regulating β3-integrin expression via HOXA10 acetylation.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Nov;98(11):4417-28. doi: 10.1210/jc.2013-1429. Epub 2013 Sep 13. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013. PMID: 24037888
-
Ion channels in the endometrium: regulation of endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation.Hum Reprod Update. 2014 Jul-Aug;20(4):517-29. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmu006. Epub 2014 Mar 2. Hum Reprod Update. 2014. PMID: 24591147 Review.
-
S100 protein family and embryo implantation.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Dec;120(12):19229-19244. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29261. Epub 2019 Jul 3. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31270848 Review.
Cited by
-
S100 proteins: An emerging cynosure in pregnancy & adverse reproductive outcome.Indian J Med Res. 2018 Dec;148(Suppl):S100-S106. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_494_18. Indian J Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30964086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Eutopic Endometrium Proteome in Endometriosis Reveals Candidate Markers and Molecular Mechanisms of Physiopathology.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Feb 6;12(2):419. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12020419. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204508 Free PMC article.
-
Gluconeogenic enzyme PCK1 supports S-adenosylmethionine biosynthesis and promotes H3K9me3 modification to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression.J Clin Invest. 2023 Jul 3;133(13):e161713. doi: 10.1172/JCI161713. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37166978 Free PMC article.
-
S100P enhances the motility and invasion of human trophoblast cell lines.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 31;8(1):11488. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29852-2. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30065265 Free PMC article.
-
S100A11 is a potential prognostic marker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016 Jan;33(1):63-71. doi: 10.1007/s10585-015-9758-6. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2016. PMID: 26472670
References
-
- Clapham DE. 2007. Calcium signaling. Cell 131:1047–1058 - PubMed
-
- Tinel H, Denker HW, Thie M. 2000. Calcium influx in human uterine epithelial RL95-2 cells triggers adhesiveness for trophoblast-like cells. Model studies on signalling events during embryo implantation. Mol Hum Reprod 6:1119–1130 - PubMed
-
- Zhang RJ, Zou LB, Zhang D, Tan YJ, Wang TT, Liu AX, Qu F, Meng Y, Ding GL, Lu YC, Lv PP, Sheng JZ, Huang HF. 2012. Functional expression of large-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels in human endometrium: a novel mechanism involved in endometrial receptivity and embryo implantation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:543–553 - PubMed
-
- Zhang M, Tanaka T, Ikura M. 1995. Calcium-induced conformational transition revealed by the solution structure of apo calmodulin. Nat Struct Biol 2:758–767 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

