Hepatitis C virus (HCV) induces formation of stress granules whose proteins regulate HCV RNA replication and virus assembly and egress
- PMID: 22855484
- PMCID: PMC3457181
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.07101-11
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) induces formation of stress granules whose proteins regulate HCV RNA replication and virus assembly and egress
Abstract
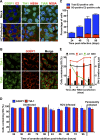
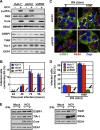
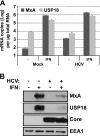
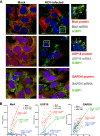
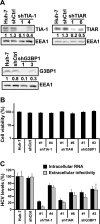
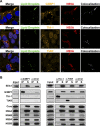
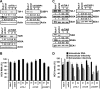
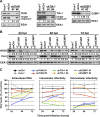
Stress granules (SGs) are cytoplasmic structures that are induced in response to environmental stress, including viral infections. Here we report that hepatitis C virus (HCV) triggers the appearance of SGs in a PKR- and interferon (IFN)-dependent manner. Moreover, we show an inverse correlation between the presence of stress granules and the induction of IFN-stimulated proteins, i.e., MxA and USP18, in HCV-infected cells despite high-level expression of the corresponding MxA and USP18 mRNAs, suggesting that interferon-stimulated gene translation is inhibited in stress granule-containing HCV-infected cells. Finally, in short hairpin RNA (shRNA) knockdown experiments, we found that the stress granule proteins T-cell-restricted intracellular antigen 1 (TIA-1), TIA1-related protein (TIAR), and RasGAP-SH3 domain binding protein 1 (G3BP1) are required for efficient HCV RNA and protein accumulation at early time points in the infection and that G3BP1 and TIA-1 are required for intracellular and extracellular infectious virus production late in the infection, suggesting that they are required for virus assembly. In contrast, TIAR downregulation decreases extracellular infectious virus titers with little effect on intracellular RNA content or infectivity late in the infection, suggesting that it is required for infectious particle release. Collectively, these results illustrate that HCV exploits the stress granule machinery at least two ways: by inducing the formation of SGs by triggering PKR phosphorylation, thereby downregulating the translation of antiviral interferon-stimulated genes, and by co-opting SG proteins for its replication, assembly, and egress.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Newcastle disease virus induces stable formation of bona fide stress granules to facilitate viral replication through manipulating host protein translation.FASEB J. 2017 Apr;31(4):1337-1353. doi: 10.1096/fj.201600980R. Epub 2016 Dec 23. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28011649
-
Zika Virus Subverts Stress Granules To Promote and Restrict Viral Gene Expression.J Virol. 2019 May 29;93(12):e00520-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00520-19. Print 2019 Jun 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30944179 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of antiviral cytoplasmic granules during orthopoxvirus infection.J Virol. 2011 Feb;85(4):1581-93. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02247-10. Epub 2010 Dec 8. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21147913 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic mRNP granules at a glance.J Cell Sci. 2011 Feb 1;124(Pt 3):293-7. doi: 10.1242/jcs.072140. J Cell Sci. 2011. PMID: 21242308 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Rasputin a decade on and more promiscuous than ever? A review of G3BPs.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Mar;1866(3):360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 30595162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA Post-Transcriptional Regulation by AU-Rich Element-Binding Proteins in Liver Inflammation and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 11;21(18):6648. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186648. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32932781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of viral RNA secondary structure on interactions with innate host cell defences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Mar;42(5):3314-29. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1291. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24335283 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia Virus Activates Integrated Stress Response Pathway and Induces Stress Granules to Regulate Virus Replication.Viruses. 2023 Feb 7;15(2):466. doi: 10.3390/v15020466. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851680 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of stress granules by interferon and down-regulation by the cellular RNA adenosine deaminase ADAR1.Virology. 2014 Apr;454-455:299-310. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2014.02.025. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Virology. 2014. PMID: 24725957 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic Interaction of Stress Granules, DDX3X, and IKK-α Mediates Multiple Functions in Hepatitis C Virus Infection.J Virol. 2015 May;89(10):5462-77. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03197-14. Epub 2015 Mar 4. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25740981 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alter HJ, Seeff LB. 2000. Recovery, persistence, and sequelae in hepatitis C virus infection: a perspective on long-term outcome. Semin. Liver Dis. 20:17–35 - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. 2009. Stress granules. Curr. Biol. 19:R397–R398 - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. 2002. Stressful initiations. J. Cell Sci. 115:3227–3234 - PubMed
-
- Arimoto K, Fukuda H, Imajoh-Ohmi S, Saito H, Takekawa M. 2008. Formation of stress granules inhibits apoptosis by suppressing stress-responsive MAPK pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 10:1324–1332 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

