A distant cis acting intronic element induces site-selective RNA editing
- PMID: 22848101
- PMCID: PMC3479170
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks691
A distant cis acting intronic element induces site-selective RNA editing
Abstract
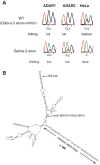
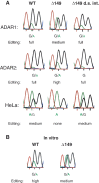
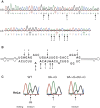
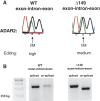
Transcripts have been found to be site selectively edited from adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) in the mammalian brain, mostly in genes involved in neurotransmission. While A-to-I editing occurs at double-stranded structures, other structural requirements are largely unknown. We have investigated the requirements for editing at the I/M site in the Gabra-3 transcript of the GABA(A) receptor. We identify an evolutionarily conserved intronic duplex, 150 nt downstream of the exonic hairpin where the I/M site resides, which is required for its editing. This is the first time a distant RNA structure has been shown to be important for A-to-I editing. We demonstrate that the element also can induce editing in related but normally not edited RNA sequences. In human, thousands of genes are edited in duplexes formed by inverted repeats in non-coding regions. It is likely that numerous such duplexes can induce editing of coding regions throughout the transcriptome.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Editing inducer elements increases A-to-I editing efficiency in the mammalian transcriptome.Genome Biol. 2017 Oct 23;18(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1324-x. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 29061182 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine-to-inosine RNA editing affects trafficking of the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABA(A)) receptor.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 21;286(3):2031-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.130096. Epub 2010 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21030585 Free PMC article.
-
RNA editing of the Drosophila para Na(+) channel transcript. Evolutionary conservation and developmental regulation.Genetics. 2000 Jul;155(3):1149-60. doi: 10.1093/genetics/155.3.1149. Genetics. 2000. PMID: 10880477 Free PMC article.
-
Site-selective versus promiscuous A-to-I editing.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Nov-Dec;2(6):761-71. doi: 10.1002/wrna.89. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21976281 Review.
-
RNA editing of non-coding RNA and its role in gene regulation.Biochimie. 2015 Oct;117:22-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.05.020. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 26051678 Review.
Cited by
-
The dsRBP and inactive editor ADR-1 utilizes dsRNA binding to regulate A-to-I RNA editing across the C. elegans transcriptome.Cell Rep. 2014 Feb 27;6(4):599-607. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.011. Epub 2014 Feb 6. Cell Rep. 2014. PMID: 24508457 Free PMC article.
-
Gene amplification-associated overexpression of the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 enhances human lung tumorigenesis.Oncogene. 2016 Aug 18;35(33):4407-13. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.469. Epub 2015 Dec 7. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26640150 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of RNA editing in plasticity.J Exp Biol. 2015 Jun;218(Pt 12):1812-21. doi: 10.1242/jeb.119065. J Exp Biol. 2015. PMID: 26085659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of tissue-specific RNA editing events in D. melanogaster and their potential role in regulating alternative splicing.RNA Biol. 2015;12(12):1391-401. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1107703. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26512413 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Architectures of Quantitative Variation in RNA Editing Pathways.Genetics. 2016 Feb;202(2):787-98. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.179481. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Genetics. 2016. PMID: 26614740 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jepson JE, Reenan RA. RNA editing in regulating gene expression in the brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008;1779:459–470. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

