zCall: a rare variant caller for array-based genotyping: genetics and population analysis
- PMID: 22843986
- PMCID: PMC3463112
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts479
zCall: a rare variant caller for array-based genotyping: genetics and population analysis
Abstract
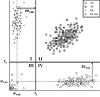
Summary: zCall is a variant caller specifically designed for calling rare single-nucleotide polymorphisms from array-based technology. This caller is implemented as a post-processing step after a default calling algorithm has been applied. The algorithm uses the intensity profile of the common allele homozygote cluster to define the location of the other two genotype clusters. We demonstrate improved detection of rare alleles when applying zCall to samples that have both Illumina Infinium HumanExome BeadChip and exome sequencing data available.
Availability: http://atguweb.mgh.harvard.edu/apps/zcall.
Contact: bneale@broadinstitute.org
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
Figures
Similar articles
-
iCall: a genotype-calling algorithm for rare, low-frequency and common variants on the Illumina exome array.Bioinformatics. 2014 Jun 15;30(12):1714-20. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu107. Epub 2014 Feb 23. Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 24567545
-
Best practices and joint calling of the HumanExome BeadChip: the CHARGE Consortium.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 12;8(7):e68095. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068095. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23874508 Free PMC article.
-
M(3): an improved SNP calling algorithm for Illumina BeadArray data.Bioinformatics. 2012 Feb 1;28(3):358-65. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr673. Epub 2011 Dec 8. Bioinformatics. 2012. PMID: 22155947 Free PMC article.
-
ALCHEMY: a reliable method for automated SNP genotype calling for small batch sizes and highly homozygous populations.Bioinformatics. 2010 Dec 1;26(23):2952-60. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq533. Epub 2010 Oct 5. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20926420 Free PMC article.
-
Using genotype array data to compare multi- and single-sample variant calls and improve variant call sets from deep coverage whole-genome sequencing data.Bioinformatics. 2017 Apr 15;33(8):1147-1153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw786. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28035032 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide burden of deleterious coding variants increased in schizophrenia.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 9;6:7501. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8501. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26158538 Free PMC article.
-
A rare functional cardioprotective APOC3 variant has risen in frequency in distinct population isolates.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2872. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3872. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24343240 Free PMC article.
-
Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries.Nat Commun. 2018 Jul 4;9(1):2606. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04668-w. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29973585 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol and myocardial infarction risk.Nat Genet. 2014 Apr;46(4):345-51. doi: 10.1038/ng.2926. Epub 2014 Mar 16. Nat Genet. 2014. PMID: 24633158 Free PMC article.
-
Using previously genotyped controls in genome-wide association studies (GWAS): application to the Stroke Genetics Network (SiGN).Front Genet. 2014 Apr 29;5:95. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00095. eCollection 2014. Front Genet. 2014. PMID: 24808905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Botstein D, Risch N. Discovering genotypes underlying human phenotypes: past successes for mendelian disease, future approaches for complex disease. Nat. Genet. 2003;33:228–237. - PubMed
-
- Illumina Inc. Illumina GenCall Data Analysis Software. TECHNOLOGY SPOTLIGHT. 2005 Available at http://www.illumina.com/Documents/products/technotes/technote_gencall_da... (8 August 2012)
-
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

