Network organization of the huntingtin proteomic interactome in mammalian brain
- PMID: 22794259
- PMCID: PMC3432264
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.05.024
Network organization of the huntingtin proteomic interactome in mammalian brain
Abstract
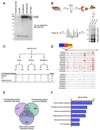
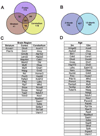
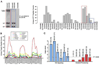
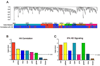
We used affinity-purification mass spectrometry to identify 747 candidate proteins that are complexed with Huntingtin (Htt) in distinct brain regions and ages in Huntington's disease (HD) and wild-type mouse brains. To gain a systems-level view of the Htt interactome, we applied Weighted Correlation Network Analysis to the entire proteomic data set to unveil a verifiable rank of Htt-correlated proteins and a network of Htt-interacting protein modules, with each module highlighting distinct aspects of Htt biology. Importantly, the Htt-containing module is highly enriched with proteins involved in 14-3-3 signaling, microtubule-based transport, and proteostasis. Top-ranked proteins in this module were validated as Htt interactors and genetic modifiers in an HD Drosophila model. Our study provides a compendium of spatiotemporal Htt-interacting proteins in the mammalian brain and presents an approach for analyzing proteomic interactome data sets to build in vivo protein networks in complex tissues, such as the brain.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proteomic analysis of wild-type and mutant huntingtin-associated proteins in mouse brains identifies unique interactions and involvement in protein synthesis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Jun 22;287(26):21599-614. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.359307. Epub 2012 May 3. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22556411 Free PMC article.
-
Huntingtin interacting proteins are genetic modifiers of neurodegeneration.PLoS Genet. 2007 May 11;3(5):e82. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0030082. PLoS Genet. 2007. PMID: 17500595 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant Huntingtin Protein Interaction Map Implicates Dysregulation of Multiple Cellular Pathways in Neurodegeneration of Huntington's Disease.J Huntingtons Dis. 2022;11(3):243-267. doi: 10.3233/JHD-220538. J Huntingtons Dis. 2022. PMID: 35871359 Free PMC article.
-
Wild-type huntingtin plays a role in brain development and neuronal survival.Mol Neurobiol. 2003 Dec;28(3):259-76. doi: 10.1385/MN:28:3:259. Mol Neurobiol. 2003. PMID: 14709789 Review.
-
Taming the Huntington's Disease Proteome: What Have We Learned?J Huntingtons Dis. 2021;10(2):239-257. doi: 10.3233/JHD-200465. J Huntingtons Dis. 2021. PMID: 33998547 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Screen in Adult Drosophila Reveals That dCBP Depletion in Glial Cells Mitigates Huntington Disease Pathology through a Foxo-Dependent Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 9;22(8):3884. doi: 10.3390/ijms22083884. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33918672 Free PMC article.
-
Huntington's disease: underlying molecular mechanisms and emerging concepts.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Aug;38(8):378-85. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2013.05.003. Epub 2013 Jun 12. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 23768628 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Description of the First Registered Case of Lopes-Maciel-Rodan Syndrome in Russia.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 18;23(20):12437. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012437. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent approaches on Huntington's disease (Review).Biomed Rep. 2022 Nov 21;18(1):5. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1587. eCollection 2023 Jan. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 36544856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Huntingtin structure is orchestrated by HAP40 and shows a polyglutamine expansion-specific interaction with exon 1.Commun Biol. 2021 Dec 8;4(1):1374. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02895-4. Commun Biol. 2021. PMID: 34880419 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS049501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DA030913-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32GM008496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS049501/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM103479/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA030913/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01RR20004/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 NS043124/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS074312/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 RR020004/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS074312/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30NS062691/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH060233/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

