MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles
- PMID: 22772984
- PMCID: PMC3467054
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks656
MicroRNAs are exported from malignant cells in customized particles
Abstract
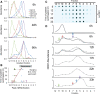
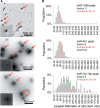
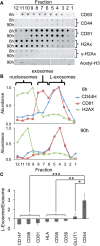
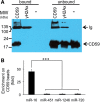
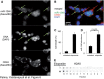
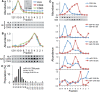
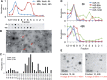
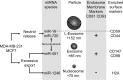
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are released from cells in association with proteins or microvesicles. We previously reported that malignant transformation changes the assortment of released miRNAs by affecting whether a particular miRNA species is released or retained by the cell. How this selectivity occurs is unclear. Here we report that selectively exported miRNAs, whose release is increased in malignant cells, are packaged in structures that are different from those that carry neutrally released miRNAs (n-miRNAs), whose release is not affected by malignancy. By separating breast cancer cell microvesicles, we find that selectively released miRNAs associate with exosomes and nucleosomes. However, n-miRNAs of breast cancer cells associate with unconventional exosomes, which are larger than conventional exosomes and enriched in CD44, a protein relevant to breast cancer metastasis. Based on their large size, we call these vesicles L-exosomes. Contrary to the distribution of miRNAs among different microvesicles of breast cancer cells, normal cells release all measured miRNAs in a single type of vesicle. Our results suggest that malignant transformation alters the pathways through which specific miRNAs are exported from cells. These changes in the particles and their miRNA cargo could be used to detect the presence of malignant cells in the body.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Microvesicles secreted by macrophages shuttle invasion-potentiating microRNAs into breast cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2011 Sep 22;10:117. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-10-117. Mol Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21939504 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of exosomal miR-9 and miR-155 targeting PTEN and DUSP14 in highly metastatic breast cancer and their effect on low metastatic cells.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):5666-5676. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27850. Epub 2018 Oct 18. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30335891
-
Lipid-based carriers of microRNAs and intercellular communication.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012 Apr;23(2):91-7. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0b013e328350a425. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2012. PMID: 22418571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Milk MicroRNAs/Exosomes: Composition and Biological Effects.Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2019;90:83-92. doi: 10.1159/000490297. Epub 2019 Mar 13. Nestle Nutr Inst Workshop Ser. 2019. PMID: 30865991
-
Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications.Mol Cancer. 2018 Oct 11;17(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0897-7. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30309355 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Breast Cancer-Specific miR Signature Unique to Extracellular Vesicles Includes "microRNA-like" tRNA Fragments.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 May;13(5):891-901. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0533. Epub 2015 Feb 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25722304 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles as carriers of microRNA, proteins and lipids in tumor microenvironment.Int J Cancer. 2016 Jan 1;138(1):14-21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29417. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 25559768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D Rhamnose β-Hederin against human breast cancer by reducing tumor-derived exosomes.Oncol Lett. 2018 Oct;16(4):5172-5178. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9254. Epub 2018 Aug 2. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30250584 Free PMC article.
-
Navigating the Landscape of Tumor Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Mar 18;20(6):1349. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061349. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30889795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examining the Paracrine Effects of Exosomes in Cardiovascular Disease and Repair.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Jun 1;7(11):e007954. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007954. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29858362 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen X, Liang H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY. Secreted microRNAs: a new form of intercellular communication. Trends Cell Biol. 2012;22:125–132. - PubMed
-
- Hata T, Murakami K, Nakatani H, Yamamoto Y, Matsuda T, Aoki N. Isolation of bovine milk-derived microvesicles carrying mRNAs and microRNAs. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;396:528–533. - PubMed
-
- Luo SS, Ishibashi O, Ishikawa G, Ishikawa T, Katayama A, Mishima T, Takizawa T, Shigihara T, Goto T, Izumi A, et al. Human villous trophoblasts express and secrete placenta-specific microRNAs into maternal circulation via exosomes. Biol. Reprod. 2009;81:717–729. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

