Nonspecific protein-DNA binding is widespread in the yeast genome
- PMID: 22768944
- PMCID: PMC3328700
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.03.044
Nonspecific protein-DNA binding is widespread in the yeast genome
Abstract
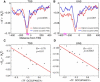
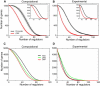
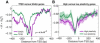
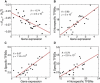
Recent genome-wide measurements of binding preferences of ~200 transcription regulators in the vicinity of transcription start sites in yeast, have provided a unique insight into the cis-regulatory code of a eukaryotic genome. Here, we show that nonspecific transcription factor (TF)-DNA binding significantly influences binding preferences of the majority of transcription regulators in promoter regions of the yeast genome. We show that promoters of SAGA-dominated and TFIID-dominated genes can be statistically distinguished based on the landscape of nonspecific protein-DNA binding free energy. In particular, we predict that promoters of SAGA-dominated genes possess wider regions of reduced free energy compared to promoters of TFIID-dominated genes. We also show that specific and nonspecific TF-DNA binding are functionally linked and cooperatively influence gene expression in yeast. Our results suggest that nonspecific TF-DNA binding is intrinsically encoded into the yeast genome, and it may play a more important role in transcriptional regulation than previously thought.
Copyright © 2012 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonspecific transcription-factor-DNA binding influences nucleosome occupancy in yeast.Biophys J. 2011 Nov 16;101(10):2465-75. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2011.10.012. Epub 2011 Nov 15. Biophys J. 2011. PMID: 22098745 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide organization of eukaryotic preinitiation complex is influenced by nonconsensus protein-DNA binding.Biophys J. 2013 Mar 5;104(5):1107-15. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.038. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23473494 Free PMC article.
-
High-resolution DNA-binding specificity analysis of yeast transcription factors.Genome Res. 2009 Apr;19(4):556-66. doi: 10.1101/gr.090233.108. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Genome Res. 2009. PMID: 19158363 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription factors dynamically control the spatial organization of the yeast genome.Nucleus. 2016 Jul 3;7(4):369-74. doi: 10.1080/19491034.2016.1212797. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Nucleus. 2016. PMID: 27442220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Promoter function and in situ protein/DNA interactions upstream of the yeast HSP90 heat shock genes.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990 Oct;58(3):175-86. doi: 10.1007/BF00548930. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1990. PMID: 2256678 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-Based Proximity Ligation Assay for Ultrasensitive, Quantitative Detection of Protein Biomarkers.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018 Sep 26;10(38):31845-31849. doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b01377. Epub 2018 Sep 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018. PMID: 30168312 Free PMC article.
-
Nonconsensus Protein Binding to Repetitive DNA Sequence Elements Significantly Affects Eukaryotic Genomes.PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Aug 18;11(8):e1004429. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004429. eCollection 2015 Aug. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015. PMID: 26285121 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Protein Search for Targets on DNA: Theoretical Insights.Molecules. 2018 Aug 22;23(9):2106. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092106. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30131459 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical estimates of exposure timescales of protein binding sites on DNA regulated by nucleosome kinetics.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Feb 29;44(4):1630-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1153. Epub 2015 Nov 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26553807 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-DNA binding in high-resolution.Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015;50(4):269-83. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2015.1051505. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26038153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ren B., Robert F., Young R.A. Genome-wide location and function of DNA binding proteins. Science. 2000;290:2306–2309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

