Lymphopenia combined with low TCR diversity (divpenia) predicts poor overall survival in metastatic breast cancer patients
- PMID: 22754761
- PMCID: PMC3382902
- DOI: 10.4161/onci.19545
Lymphopenia combined with low TCR diversity (divpenia) predicts poor overall survival in metastatic breast cancer patients
Abstract
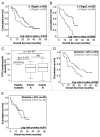
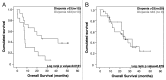
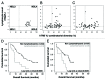
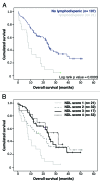
Lymphopenia (< 1Giga/L) detected before initiation of chemotherapy is a predictive factor for death in metastatic solid tumors. Combinatorial T cell repertoire (TCR) diversity was investigated and tested either alone or in combination with lymphopenia as a prognostic factor at diagnosis for overall survival (OS) in metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients. The combinatorial TCR diversity was measured by semi quantitative multi-N-plex PCR on blood samples before the initiation of the first line chemotherapy in a development (n = 66) and validation (n = 67) MBC patient cohorts. A prognostic score, combining lymphocyte count and TCR diversity was evaluated. Univariate and multivariate analyses of prognostic factors for OS were performed in both cohorts. Lymphopenia and severe restriction of TCR diversity called "divpenia" (diversity ≤ 33%) were independently associated with shorter OS. Lympho-divpenia combining lymphopenia and severe divpenia accurately identified patients with poor OS in both cohorts (7.6 and 10.6 vs 24.5 and 22.9 mo). In multivariate analysis including other prognostic clinical factors, lympho-divpenia was found to be an independent prognostic factor in the pooled cohort (p = 0.005) along with lack of HER2 and hormonal receptors expression (p = 0.011) and anemia (p = 0.009). Lympho-divpenia is a novel prognostic factor that will be used to improve quality of MBC patients' medical care.
Figures
Similar articles
-
T-cell receptor diversity as a prognostic biomarker in melanoma patients.Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020 Jul;33(4):612-624. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12866. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2020. PMID: 31971658
-
Patients with metastatic breast cancer leading to CD4+ T cell lymphopaenia have poor outcome.Eur J Cancer. 2013 May;49(7):1673-82. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.028. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23265706
-
Prognostic Value of Modified IHC4 Score in Patients with Estrogen Receptor-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2020 Aug;25(8):e1170-e1180. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-1006. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Oncologist. 2020. PMID: 32476192 Free PMC article.
-
CD4 lymphopenia to identify end-of-life metastatic cancer patients.Eur J Cancer. 2013 Mar;49(5):1080-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.11.003. Epub 2012 Dec 13. Eur J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23246297
-
Lymphopenia in Cancer Patients and its Effects on Response to Immunotherapy: an opportunity for combination with Cytokines?J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Mar 28;7(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0549-5. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30922400 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigation of Long-Term CD4+ T Cell Receptor Repertoire Changes Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients with Different Severities of Disease.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 19;14(20):2330. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14202330. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451653 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of pretreatment blood lymphocyte count in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Jan 10;20:15. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-1094-5. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 31938023 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained lymphocyte decreases after treatment for early breast cancer.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2024 Oct 21;10(1):94. doi: 10.1038/s41523-024-00698-4. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39433772 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors for radiation induced lymphopenia in patients with breast cancer receiving adjuvant radiotherapy.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Aug;9(16):1288. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2150. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34532425 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics Analysis of the Prognostic Significance of CAND1 in ERα-Positive Breast Cancer.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 27;12(10):2327. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12102327. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36292029 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blay JY, Chauvin F, Le Cesne A, Anglaret B, Bouhour D, Lasset C, et al. Early lymphopenia after cytotoxic chemotherapy as a risk factor for febrile neutropenia. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:636–43. - PubMed
-
- Blay JY, Le Cesne A, Mermet C, Maugard C, Ravaud A, Chevreau C, et al. A risk model for thrombocytopenia requiring platelet transfusion after cytotoxic chemotherapy. Blood. 1998;92:405–10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
