Photocontrolled nanoparticles for on-demand release of proteins
- PMID: 22746981
- PMCID: PMC3417466
- DOI: 10.1021/bm300646q
Photocontrolled nanoparticles for on-demand release of proteins
Abstract
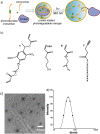
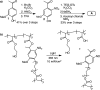
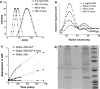
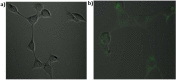
We describe here light-regulated swelling and degradation features of polymeric nanoparticles that are produced using an inverse microemulsion polymerization method. We demonstrate the phototriggered release characteristics of the nanoparticles by sequestering protein molecules and releasing them using light as a trigger. Furthermore, the intracellular translocation of the nanoparticles, along with its fluorescent protein payload, was achieved using a cell-penetrating peptide-based surface modification. We expect that the noncovalent encapsulation of proteins using nanoparticles and their photo triggered release using an external light would provide opportunities for achieving intracellular release of molecular therapeutics for on-demand requirements.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reduction and pH dual-bioresponsive crosslinked polymersomes for efficient intracellular delivery of proteins and potent induction of cancer cell apoptosis.Acta Biomater. 2014 May;10(5):2159-68. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Acta Biomater. 2014. PMID: 24440420
-
Layer-by-layer assembled polyaspartamide nanocapsules for pH-responsive protein delivery.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013 Aug 1;108:205-11. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.03.007. Epub 2013 Mar 16. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2013. PMID: 23563286
-
Photo-crosslinked biodegradable hydrogels prepared from fumaric acid monoethyl ester-functionalized oligomers for protein delivery.Macromol Biosci. 2012 May;12(5):692-702. doi: 10.1002/mabi.201100468. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Macromol Biosci. 2012. PMID: 22416030
-
Polyelectrolyte nanoparticles based on water-soluble chitosan-poly(L-aspartic acid)-polyethylene glycol for controlled protein release.Carbohydr Res. 2009 Jul 6;344(10):1197-204. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2009.04.018. Epub 2009 Apr 20. Carbohydr Res. 2009. PMID: 19508912
-
Advances in preparation and characterization of chitosan nanoparticles for therapeutics.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(1):305-14. doi: 10.3109/21691401.2014.948548. Epub 2014 Aug 19. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 25137489 Review.
Cited by
-
Reactive Self-Assembly of Polymers and Proteins to Reversibly Silence a Killer Protein.Biomacromolecules. 2015 Oct 12;16(10):3161-71. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b00779. Epub 2015 Sep 10. Biomacromolecules. 2015. PMID: 26331939 Free PMC article.
-
Low power upconverted near-IR light for efficient polymeric nanoparticle degradation and cargo release.Adv Mater. 2013 Jul 19;25(27):3733-8. doi: 10.1002/adma.201300902. Epub 2013 May 31. Adv Mater. 2013. PMID: 23722298 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulus-responsive hydrogels: Theory, modern advances, and applications.Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2015 Jul;93:1-49. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 May 16. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2015. PMID: 27134415 Free PMC article.
-
Charged Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) Nanogels for the Stabilization of High Isoelectric Point Proteins.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021 Sep 13;7(9):4282-4292. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c01690. Epub 2021 Feb 9. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 33560107 Free PMC article.
-
Photoresponsive nanoparticles for drug delivery.Nano Today. 2015 Aug 1;10(4):451-467. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jul 15. Nano Today. 2015. PMID: 26644797 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Namiki Y.; Fuchigami T.; Tada N.; Kawamura R.; Matsunuma S.; Kitamoto Y.; Nakagawa M. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 1080–1093. - PubMed
-
- Chou L. Y. T.; Ming K.; Chan W. C. W. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 233–245. - PubMed
-
- Maeda H.; Matsumura Y.; Sasamoto K. Proc. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 1986, 27, 401–401.
-
- Maeda H.; Wu J.; Sawa T.; Matsumura Y.; Hori K. J. Controlled Release 2000, 65, 271–284. - PubMed
-
- Lawrence M. J.; Rees G. D. Adv. Drug Delivery Rev. 2000, 45, 89–121. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

