GO-Elite: a flexible solution for pathway and ontology over-representation
- PMID: 22743224
- PMCID: PMC3413395
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts366
GO-Elite: a flexible solution for pathway and ontology over-representation
Abstract
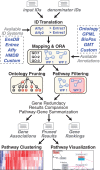
We introduce GO-Elite, a flexible and powerful pathway analysis tool for a wide array of species, identifiers (IDs), pathways, ontologies and gene sets. In addition to the Gene Ontology (GO), GO-Elite allows the user to perform over-representation analysis on any structured ontology annotations, pathway database or biological IDs (e.g. gene, protein or metabolite). GO-Elite exploits the structured nature of biological ontologies to report a minimal set of non-overlapping terms. The results can be visualized on WikiPathways or as networks. Built-in support is provided for over 60 species and 50 ID systems, covering gene, disease and phenotype ontologies, multiple pathway databases, biomarkers, and transcription factor and microRNA targets. GO-Elite is available as a web interface, GenMAPP-CS plugin and as a cross-platform application.
Availability: http://www.genmapp.org/go_elite
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Gene Ontology in 2010: extensions and refinements.Nucleic Acids Res. 2010 Jan;38(Database issue):D331-5. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp1018. Epub 2009 Nov 17. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010. PMID: 19920128 Free PMC article.
-
AmiGO: online access to ontology and annotation data.Bioinformatics. 2009 Jan 15;25(2):288-9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btn615. Epub 2008 Nov 25. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19033274 Free PMC article.
-
QuickGO: a web-based tool for Gene Ontology searching.Bioinformatics. 2009 Nov 15;25(22):3045-6. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp536. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19744993 Free PMC article.
-
Ontology annotation: mapping genomic regions to biological function.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007 Feb;11(1):4-11. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.11.039. Epub 2007 Jan 5. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17208035 Review.
-
A survey of metabolic databases emphasizing the MetaCyc family.Arch Toxicol. 2011 Sep;85(9):1015-33. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0705-2. Epub 2011 Apr 27. Arch Toxicol. 2011. PMID: 21523460 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and validation of putative biomarkers by in silico analysis, mRNA expression and oxidative stress indicators for negative energy balance in buffaloes during transition period.Anim Biosci. 2024 Mar;37(3):522-535. doi: 10.5713/ab.23.0284. Epub 2024 Jan 20. Anim Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38271975 Free PMC article.
-
A network approach reveals driver genes associated with survival of patients with triple-negative breast cancer.iScience. 2021 Apr 19;24(5):102451. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102451. eCollection 2021 May 21. iScience. 2021. PMID: 34007962 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the osteoblast transcriptome in a model of enhanced bone formation due to constitutive Gs-G protein signaling in osteoblasts.Exp Cell Res. 2015 May 1;333(2):289-302. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.02.009. Epub 2015 Feb 20. Exp Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25704759 Free PMC article.
-
New insights in Rett syndrome using pathway analysis for transcriptomics data.Wien Med Wochenschr. 2016 Sep;166(11-12):346-52. doi: 10.1007/s10354-016-0488-4. Epub 2016 Aug 12. Wien Med Wochenschr. 2016. PMID: 27517371 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative network analysis reveals biological pathways associated with Williams syndrome.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2019 May;60(5):585-598. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12999. Epub 2018 Oct 25. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 30362171 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hochstenbach K., et al. Transcriptomic profile indicative of immunotoxic exposure: in vitro studies in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2010;118:19–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

