NAC functions as a modulator of SRP during the early steps of protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum
- PMID: 22740632
- PMCID: PMC3418300
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.E12-02-0112
NAC functions as a modulator of SRP during the early steps of protein targeting to the endoplasmic reticulum
Abstract
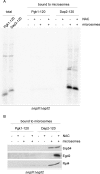
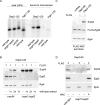
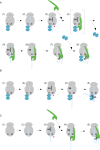
Nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) was initially found to bind to any segment of the nascent chain except signal sequences. In this way, NAC is believed to prevent mistargeting due to binding of signal recognition particle (SRP) to signalless ribosome nascent chain complexes (RNCs). Here we revisit the interplay between NAC and SRP. NAC does not affect SRP function with respect to signalless RNCs; however, NAC does affect SRP function with respect to RNCs targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). First, early recruitment of SRP to RNCs containing a signal sequence within the ribosomal tunnel is NAC dependent. Second, NAC is able to directly and tightly bind to nascent signal sequences. Third, SRP initially displaces NAC from RNCs; however, when the signal sequence emerges further, trimeric NAC·RNC·SRP complexes form. Fourth, upon docking to the ER membrane NAC remains bound to RNCs, allowing NAC to shield cytosolically exposed nascent chain domains not only before but also during cotranslational translocation. The combined data indicate a functional interplay between NAC and SRP on ER-targeted RNCs, which is based on the ability of the two complexes to bind simultaneously to distinct segments of a single nascent chain.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Binding of signal recognition particle gives ribosome/nascent chain complexes a competitive advantage in endoplasmic reticulum membrane interaction.Mol Biol Cell. 1998 Jan;9(1):103-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.9.1.103. Mol Biol Cell. 1998. PMID: 9436994 Free PMC article.
-
The intrinsic ability of ribosomes to bind to endoplasmic reticulum membranes is regulated by signal recognition particle and nascent-polypeptide-associated complex.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Oct 10;92(21):9435-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.21.9435. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7568149 Free PMC article.
-
A signal-anchor sequence stimulates signal recognition particle binding to ribosomes from inside the exit tunnel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Feb 3;106(5):1398-403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808584106. Epub 2009 Jan 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19164516 Free PMC article.
-
Fidelity of Cotranslational Protein Targeting to the Endoplasmic Reticulum.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 28;23(1):281. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010281. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-translational targeting and translocation of proteins to the endoplasmic reticulum.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Nov;1833(11):2392-402. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.021. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23481039 Review.
Cited by
-
N-terminal acetylation of the yeast Derlin Der1 is essential for Hrd1 ubiquitin-ligase activity toward luminal ER substrates.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Apr;24(7):890-900. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-11-0838. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23363603 Free PMC article.
-
Nascent polypeptide-Associated Complex and Signal Recognition Particle have cardiac-specific roles in heart development and remodeling.PLoS Genet. 2022 Oct 14;18(10):e1010448. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010448. eCollection 2022 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36240221 Free PMC article.
-
Positively charged amino acids at the N terminus of select mitochondrial proteins mediate early recognition by import proteins αβ'-NAC and Sam37.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):101984. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101984. Epub 2022 Apr 26. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35487246 Free PMC article.
-
Cotranslational Intersection between the SRP and GET Targeting Pathways to the Endoplasmic Reticulum of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Cell Biol. 2016 Aug 26;36(18):2374-83. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00131-16. Print 2016 Sep 15. Mol Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27354063 Free PMC article.
-
Role for ribosome-associated complex and stress-seventy subfamily B (RAC-Ssb) in integral membrane protein translation.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 1;292(48):19610-19627. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.813857. Epub 2017 Oct 2. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28972146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bukau B, Deuerling E, Pfund C, Craig EA. Getting newly synthesized proteins into shape. Cell. 2000;101:119–122. - PubMed
-
- Cheng Z, Gilmore R. Slow translocon gating causes cytosolic exposure of transmembrane and lumenal domains during membrane protein integration. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2006;13:930–936. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

