Identifying cancer biomarkers by mass spectrometry-based glycomics
- PMID: 22740464
- PMCID: PMC3673023
- DOI: 10.1002/elps.201100715
Identifying cancer biomarkers by mass spectrometry-based glycomics
Abstract
Correlations between aberrant glycosylation and cancer have been established for decades. The major advances in mass spectrometry (MS) and separation science have rapidly advanced detailed characterization of the changes associated with cancer development and progression. Over the past 10 years, many reports have described MS-based glycomic methods directed toward comparing the glycomic profiles of different human specimens collected from disease-free individuals and patients with cancers. Glycomic profiling of glycoproteins isolated from human specimens originating from disease-free individuals and patients with cancers have also been performed. Profiling of native, labeled, and permethylated glycans has been acquired using MALDI-MS and LC-MS. This review focuses on describing, discussing, and evaluating the different glycomic methods employed to characterize and quantify glycomic changes associated with cancers of different organs, including breast, colon, esophagus, liver, ovarian, pancreas, and prostate.
© 2012 WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
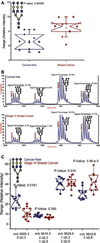
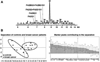
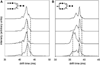
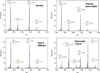
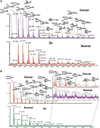
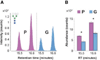
Similar articles
-
Defining putative glycan cancer biomarkers by MS.Bioanalysis. 2012 Oct;4(20):2457-69. doi: 10.4155/bio.12.246. Bioanalysis. 2012. PMID: 23157355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing MALDI-MS, RP-LC-MALDI-MS and RP-LC-ESI-MS glycomic profiles of permethylated N-glycans derived from model glycoproteins and human blood serum.Electrophoresis. 2012 Jul;33(12):1768-77. doi: 10.1002/elps.201100703. Electrophoresis. 2012. PMID: 22740465 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative glycomic profiling of isotopically permethylated N-glycans by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013 Apr 30;27(8):865-77. doi: 10.1002/rcm.6512. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23495056 Free PMC article.
-
8-plex LC-MS/MS Analysis of Permethylated N-Glycans Achieved by Using Stable Isotopic Iodomethane.Anal Chem. 2019 Sep 17;91(18):11794-11802. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b02411. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31356052 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Spectrometry Approaches to Glycomic and Glycoproteomic Analyses.Chem Rev. 2018 Sep 12;118(17):7886-7930. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00732. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Chem Rev. 2018. PMID: 29553244 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in the Expression of Renal Brush Border Membrane N-Glycome in Model Rats with Chronic Kidney Diseases.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 11;11(11):1677. doi: 10.3390/biom11111677. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827675 Free PMC article.
-
High-temperature LC-MS/MS of permethylated glycans derived from glycoproteins.Electrophoresis. 2016 Jun;37(11):1506-13. doi: 10.1002/elps.201500568. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Electrophoresis. 2016. PMID: 26914157 Free PMC article.
-
N-glycosylation Profiling of Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines Reveals Association of Fucosylation with Differentiation and Caudal Type Homebox 1 (CDX1)/Villin mRNA Expression.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Jan;15(1):124-40. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.051235. Epub 2015 Nov 4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26537799 Free PMC article.
-
Electrochemistry of nonconjugated proteins and glycoproteins. Toward sensors for biomedicine and glycomics.Chem Rev. 2015 Mar 11;115(5):2045-108. doi: 10.1021/cr500279h. Epub 2015 Feb 9. Chem Rev. 2015. PMID: 25659975 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Can glycoprofiling be helpful in detecting prostate cancer?Chem Zvesti. 2015 Jan;69(1):90-111. doi: 10.1515/chempap-2015-0052. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Chem Zvesti. 2015. PMID: 27257317 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dwek RA. Chem. Rev. 1996;96:683–720. - PubMed
-
- Helenius A, Aebi M. Science. 2001;291:2364–2369. - PubMed
-
- Rudd PM, Woods RJ, Wormald MR, Opdenakker G, Downing AK, Campbell ID, Dwek RA. Biochem. Biophys. Acta. 1995;1248:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Rudd PM, Wormald MR, Stanfield RL, Huang M, Mattson N, Speir JA, DiGennaro JA, Fetrow JS, Dwek RA, Wilson IA. J. Mol. Biol. 1999;293:351–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

