YM155 reverses cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer by decreasing cytoplasmic survivin levels
- PMID: 22723337
- PMCID: PMC3889136
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0167
YM155 reverses cisplatin resistance in head and neck cancer by decreasing cytoplasmic survivin levels
Abstract
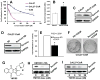
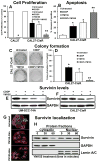
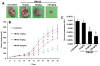
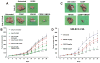
Cisplatin is one of the commonly used chemotherapeutic drugs for the treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). However, acquisition of cisplatin resistance is common in patients with HNSCC, and it often leads to local and distant failure. In this study, we showed that survivin expression is significantly upregulated in HNSCC primary tumors and cell lines. In addition, survivin levels were significantly higher in human papilloma virus-negative patients that normally respond poorly to cisplatin treatment. Survivin expression was further increased in cisplatin-resistant cells (CAL27-CisR) as compared with its parent cells (CAL27). Therefore, we hypothesized that targeting of survivin in HNSCC could reverse the resistant phenotype in tumor cells, thereby enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin. We used both in vitro and in vivo models to test the efficacy of YM155, a small molecule survivin inhibitor, either as a single agent or in combination with cisplatin. YM155 significantly decreased survivin levels and cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, YM155 pretreatment significantly reversed cisplatin resistance in cancer cells. Interestingly, YM155 treatment altered the dynamic localization of survivin in cells by inducing a rapid reduction in cytoplasmic survivin, which plays a critical role in its antiapoptotic function. In a severe combined immunodeficient mouse xenograft model, YM155 significantly enhanced the antitumor and antiangiogenic effects of cisplatin, with no added systemic toxicity. Taken together, our results suggest a potentially novel strategy to use YM155 to overcome the resistance in tumor cells, thereby enhancing the effectiveness of the chemotherapy in HNSCC.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Dual induction of apoptotic and autophagic cell death by targeting survivin in head neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cell Death Dis. 2015 May 28;6(5):e1771. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2015.139. Cell Death Dis. 2015. PMID: 26018732 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of YM155, a selective survivin suppressant, in combination with cisplatin in hepatoblastoma.Oncol Rep. 2015 Jul;34(1):407-14. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3947. Epub 2015 May 5. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25955434
-
Survivin selective inhibitor YM155 promotes cisplatin‑induced apoptosis in embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma.Int J Oncol. 2016 May;48(5):1847-54. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3438. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26983495
-
Survivin and YM155: how faithful is the liaison?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Apr;1845(2):202-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.01.003. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24440709 Review.
-
[Survivin supressant: a promising target for cancer therapy and pharmacological profiles of YM155].Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010 Oct;136(4):198-203. doi: 10.1254/fpj.136.198. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2010. PMID: 20948154 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) reverses chemoresistance in head and neck cancer cells by targeting cancer stem cells via the downregulation of nanog.Genes Cancer. 2015 Mar;6(3-4):169-81. doi: 10.18632/genesandcancer.54. Genes Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26000099 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting survivin in cancer: novel drug development approaches.BioDrugs. 2014 Feb;28(1):27-39. doi: 10.1007/s40259-013-0058-x. BioDrugs. 2014. PMID: 23955284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy Options for Recurrent and/or Metastatic Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck.Clin Med Insights Ther. 2013;2013(5):10.4137/CMT.S10409. doi: 10.4137/CMT.S10409. Clin Med Insights Ther. 2013. PMID: 24273416 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of 6-phosphogluconate Dehydrogenase Reverses Cisplatin Resistance in Ovarian and Lung Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jun 30;8:421. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00421. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28713273 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis protein 1 (cIAP1) stability contributes to YM155 resistance in human gastric cancer cells.J Biol Chem. 2015 Apr 17;290(16):9974-85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.600874. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25635055 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Kalavrezos N, Bhandari R. Current trends and future perspectives in the surgical management of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2010;46:429–32. - PubMed
-
- Marur S, Forastiere AA. Head and neck cancer: changing epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2008;83:489–501. - PubMed
-
- Colnaghi R, Connell CM, Barrett RM, Wheatley SP. Separating the anti-apoptotic and mitotic roles of survivin. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:33450–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

