Hippocampal synthesis of sex steroids and corticosteroids: essential for modulation of synaptic plasticity
- PMID: 22701110
- PMCID: PMC3356120
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2011.00043
Hippocampal synthesis of sex steroids and corticosteroids: essential for modulation of synaptic plasticity
Abstract
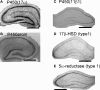
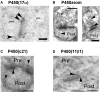
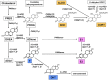
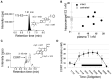
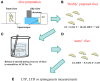
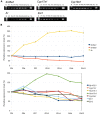
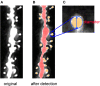
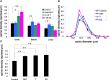
Sex steroids play essential roles in the modulation of synaptic plasticity and neuroprotection in the hippocampus. Accumulating evidence shows that hippocampal neurons synthesize both estrogen and androgen. Recently, we also revealed the hippocampal synthesis of corticosteroids. The accurate concentrations of these hippocampus-synthesized steroids are determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass-spectrometry in combination with novel derivatization. The hippocampal levels of 17β-estradiol (E2), testosterone (T), dihydrotestosterone (DHT), and corticosterone (CORT), are 5-15 nM, and these levels are sufficient to modulate synaptic plasticity. Hippocampal E2 modulates memory-related synaptic plasticity not only slowly/genomically but also rapidly/non-genomically. Slow actions of E2 occur via classical nuclear receptors (ERα or ERβ), while rapid E2 actions occur via synapse-localized or extranuclear ERα or ERβ. Nanomolar concentrations of E2 change rapidly the density and morphology of spines in hippocampal neurons. ERα, but not ERβ, drives this enhancement/suppression of spinogenesis in adult animals. Nanomolar concentrations of androgens (T and DHT) and CORT also increase the spine density. Kinase networks are involved downstream of ERα and androgen receptor. Newly developed Spiso-3D mathematical analysis is useful to distinguish these complex effects by sex steroids and kinases. Significant advance has been achieved in investigations of rapid modulation by E2 of the long-term depression or the long-term potentiation.
Keywords: androgen; corticosteroid; estrogen; hippocampus; sex steroid; spinogenesis; synaptic plasticity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus by hippocampus-derived estrogen and androgen.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Aug;131(1-2):37-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2011.10.004. Epub 2011 Oct 31. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22075082 Review.
-
Modulation of synaptic plasticity by brain estrogen in the hippocampus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Oct;1800(10):1030-44. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19909788 Review.
-
Rapid increase of spines by dihydrotestosterone and testosterone in hippocampal neurons: Dependence on synaptic androgen receptor and kinase networks.Brain Res. 2015 Sep 24;1621:121-32. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.12.011. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25511993
-
Src Kinase Dependent Rapid Non-genomic Modulation of Hippocampal Spinogenesis Induced by Androgen and Estrogen.Front Neurosci. 2018 May 1;12:282. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00282. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29765299 Free PMC article.
-
Neurosteroids in Adult Hippocampus of Male and Female Rodents: Biosynthesis and Actions of Sex Steroids.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Apr 23;9:183. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00183. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29740398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Uptake and metabolism of sulphated steroids by the blood-brain barrier in the adult male rat.J Neurochem. 2017 Sep;142(5):672-685. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14117. Epub 2017 Aug 3. J Neurochem. 2017. PMID: 28665486 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of androgen receptors protects intact male mice from memory impairments caused by aromatase inhibition.Horm Behav. 2019 May;111:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.yhbeh.2019.01.002. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Horm Behav. 2019. PMID: 30653980 Free PMC article.
-
Brain sex matters: estrogen in cognition and Alzheimer's disease.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 May 25;389(1-2):13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.12.018. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24418360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Re-evaluation of the risks to public health related to the presence of bisphenol A (BPA) in foodstuffs.EFSA J. 2023 Apr 19;21(4):e06857. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2023.6857. eCollection 2023 Apr. EFSA J. 2023. PMID: 37089179 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of estradiol in fear circuitry: implications for sex differences in psychopathology.Transl Psychiatry. 2014 Aug 5;4(8):e422. doi: 10.1038/tp.2014.67. Transl Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 25093600 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

