Exploiting synthetic lethality for the therapy of ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- PMID: 22698399
- PMCID: PMC4059833
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.05.024
Exploiting synthetic lethality for the therapy of ABC diffuse large B cell lymphoma
Abstract
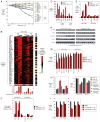
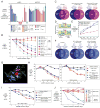
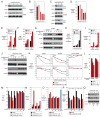
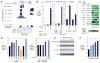
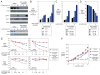
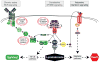
Knowledge of oncogenic mutations can inspire therapeutic strategies that are synthetically lethal, affecting cancer cells while sparing normal cells. Lenalidomide is an active agent in the activated B cell-like (ABC) subtype of diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL), but its mechanism of action is unknown. Lenalidomide kills ABC DLBCL cells by augmenting interferon β (IFNβ) production, owing to the oncogenic MYD88 mutations in these lymphomas. In a cereblon-dependent fashion, lenalidomide downregulates IRF4 and SPIB, transcription factors that together prevent IFNβ production by repressing IRF7 and amplify prosurvival NF-κB signaling by transactivating CARD11. Blockade of B cell receptor signaling using the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib also downregulates IRF4 and consequently synergizes with lenalidomide in killing ABC DLBCLs, suggesting attractive therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

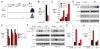
Similar articles
-
Lenalidomide efficacy in activated B-cell-like subtype diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is dependent upon IRF4 and cereblon expression.Br J Haematol. 2013 Feb;160(4):487-502. doi: 10.1111/bjh.12172. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Br J Haematol. 2013. PMID: 23252516
-
Lenalidomide modulates gene expression in human ABC-DLBCL cells by regulating IKAROS interaction with an intronic control region of SPIB.Exp Hematol. 2017 Dec;56:46-57.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Exp Hematol. 2017. PMID: 28893618
-
CC-122, a pleiotropic pathway modifier, mimics an interferon response and has antitumor activity in DLBCL.Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126(6):779-89. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-02-628669. Epub 2015 May 22. Blood. 2015. PMID: 26002965 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Mechanisms of Action of Lenalidomide in B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma.J Clin Oncol. 2015 Sep 1;33(25):2803-11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.59.5363. Epub 2015 Jul 20. J Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 26195701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lenalidomide combined with R-GDP in a patient with refractory CD5-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A promising response and review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 Jul 3;19(7):549-553. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1449609. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29611764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lenalidomide induces ubiquitination and degradation of CK1α in del(5q) MDS.Nature. 2015 Jul 9;523(7559):183-188. doi: 10.1038/nature14610. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26131937 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a BTK/MNK dual inhibitor for lymphoma and leukemia.Leukemia. 2016 Jan;30(1):173-81. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.180. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Leukemia. 2016. PMID: 26165234 Free PMC article.
-
Real-world data for lenalidomide maintenance in responding patients of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(9):10553-10562. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5790. Epub 2023 Mar 13. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36912128 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic pan-cancer study demonstrates the oncogenic function of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Mar 28;14(6):2880-2901. doi: 10.18632/aging.203981. Epub 2022 Mar 28. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 35344508 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the HTLV-I-Regulated BATF3/IRF4 Transcriptional Network in Adult T Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma.Cancer Cell. 2018 Aug 13;34(2):286-297.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2018.06.014. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Cancer Cell. 2018. PMID: 30057145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, Boldrick JC, Sabet H, Tran T, Yu X, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. - PubMed
-
- Brass AL, Kehrli E, Eisenbeis CF, Storb U, Singh H. Pip, a lymphoid-restricted IRF, contains a regulatory domain that is important for autoinhibition and ternary complex formation with the Ets factor PU.1. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2335–2347. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

