TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5 mediate cerebral microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis induced by oligomeric Alzheimer's Aβ
- PMID: 22695614
- PMCID: PMC3388229
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2012.55
TRAIL death receptors DR4 and DR5 mediate cerebral microvascular endothelial cell apoptosis induced by oligomeric Alzheimer's Aβ
Abstract
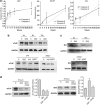
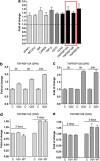
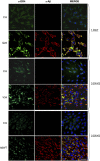
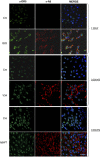
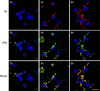
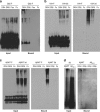
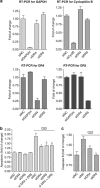
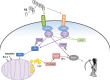
Vascular deposition of amyloid-β (Aβ) in sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease, through poorly understood molecular mechanisms, leads to focal ischemia, alterations in cerebral blood flow, and cerebral micro-/macro-hemorrhages, significantly contributing to cognitive impairment. Here, we show that tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) death receptors DR4 and DR5 specifically mediate oligomeric Aβ induction of extrinsic apoptotic pathways in human microvascular cerebral endothelial cells with activation of both caspase-8 and caspase-9. The caspase-8 inhibitor cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (cFLIP) is downregulated, and mitochondrial paths are engaged through BH3-interacting domain death agonist (Bid) cleavage. Upregulation of DR4 and DR5 and colocalization with Aβ at the cell membrane suggests their involvement as initiators of the apoptotic machinery. Direct binding assays using receptor chimeras confirm the specific interaction of oligomeric Aβ with DR4 and DR5 whereas apoptosis protection achieved through RNA silencing of both receptors highlights their active role in downstream apoptotic pathways unveiling new targets for therapeutic intervention.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Homocysteine potentiates amyloid -induced death receptor 4- and 5-mediated cerebral endothelial cell apoptosis, blood brain barrier dysfunction and angiogenic impairment.Aging Cell. 2024 May;23(5):e14106. doi: 10.1111/acel.14106. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38358083 Free PMC article.
-
The TRAIL apoptotic pathway mediates proteasome inhibitor induced apoptosis in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.Apoptosis. 2006 Jul;11(7):1175-93. doi: 10.1007/s10495-006-8048-9. Apoptosis. 2006. PMID: 16699949
-
Ewing's sarcoma family tumors are sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and express death receptor 4 and death receptor 5.Cancer Res. 2001 Mar 15;61(6):2704-12. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11289151
-
Regulation of Cancer Metastasis by TRAIL/Death Receptor Signaling.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 26;11(4):499. doi: 10.3390/biom11040499. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33810241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by ectopic expression of antiapoptotic factors.Vitam Horm. 2004;67:453-83. doi: 10.1016/S0083-6729(04)67023-3. Vitam Horm. 2004. PMID: 15110190 Review.
Cited by
-
Homocysteine potentiates amyloid -induced death receptor 4- and 5-mediated cerebral endothelial cell apoptosis, blood brain barrier dysfunction and angiogenic impairment.Aging Cell. 2024 May;23(5):e14106. doi: 10.1111/acel.14106. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38358083 Free PMC article.
-
Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Gold Quantum Dots Exert Dual Cytotoxicity Mediated by the Cell Receptor-Activated Apoptotic Pathway in Glioblastoma Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 16;12(2):457. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020457. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32079108 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the role of key amino acids in regulation of proline dehydrogenase/proline oxidase (prodh/pox)-dependent apoptosis/autophagy as an approach to targeted cancer therapy.Mol Cell Biochem. 2020 Mar;466(1-2):35-44. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03685-y. Epub 2020 Jan 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020. PMID: 31933109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Antidepressant Drug Increased TRAIL Receptor-2 Expression and Sensitized Lung Cancer Cells to TRAIL-induced Apoptosis.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023;23(20):2225-2236. doi: 10.2174/0118715206262252231004110310. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 37859313 Free PMC article.
-
Traumatic Brain Injury and Alzheimer's Disease: The Cerebrovascular Link.EBioMedicine. 2018 Feb;28:21-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.01.021. Epub 2018 Jan 31. EBioMedicine. 2018. PMID: 29396300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Attems J, Jellinger K, Thal DR, Van Nostrand W. Review: sporadic cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011;37:75–93. - PubMed
-
- Nicoll JAR, Yamada M, Frackowiak J, Mazur-Kolecka B, Weller RO. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy plays a direct role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25:589–597. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

