BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib improves the antitumor activity of adoptive cell immunotherapy
- PMID: 22693252
- PMCID: PMC3422880
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2837
BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib improves the antitumor activity of adoptive cell immunotherapy
Abstract
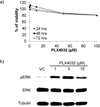
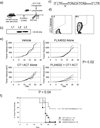
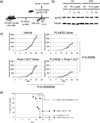
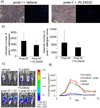
Combining immunotherapy with targeted therapy blocking oncogenic BRAFV600 may result in improved treatments for advanced melanoma. In this study, we developed a BRAFV600E-driven murine model of melanoma, SM1, which is syngeneic to fully immunocompetent mice. SM1 cells exposed to the BRAF inhibitor vemurafenib (PLX4032) showed partial in vitro and in vivo sensitivity resulting from the inhibition of MAPK pathway signaling. Combined treatment of vemurafenib plus adoptive cell transfer therapy with lymphocytes genetically modified with a T-cell receptor (TCR) recognizing chicken ovalbumin (OVA) expressed by SM1-OVA tumors or pmel-1 TCR transgenic lymphocytes recognizing gp100 endogenously expressed by SM1 resulted in superior antitumor responses compared with either therapy alone. T-cell analysis showed that vemurafenib did not significantly alter the expansion, distribution, or tumor accumulation of the adoptively transferred cells. However, vemurafenib paradoxically increased mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling, in vivo cytotoxic activity, and intratumoral cytokine secretion by adoptively transferred cells. Taken together, our findings, derived from 2 independent models combining BRAF-targeted therapy with immunotherapy, support the testing of this therapeutic combination in patients with BRAFV600 mutant metastatic melanoma.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
BRAF inhibition increases tumor infiltration by T cells and enhances the antitumor activity of adoptive immunotherapy in mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Jan 15;19(2):393-403. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-1626. Epub 2012 Nov 30. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23204132 Free PMC article.
-
17-AAG inhibits vemurafenib-associated MAP kinase activation and is synergistic with cellular immunotherapy in a murine melanoma model.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 26;13(2):e0191264. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191264. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29481571 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of colony stimulating factor-1 receptor improves antitumor efficacy of BRAF inhibition.BMC Cancer. 2015 May 5;15:356. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-1377-8. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25939769 Free PMC article.
-
Adoptive T-cell transfer therapy and oncogene-targeted therapy for melanoma: the search for synergy.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Oct 1;19(19):5292-9. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0261. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24089442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vemurafenib for the treatment of BRAF mutant metastatic melanoma.Future Oncol. 2015;11(4):579-89. doi: 10.2217/fon.14.252. Future Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25686114 Review.
Cited by
-
BRAF Inhibitor Resistance in Melanoma: Mechanisms and Alternative Therapeutic Strategies.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022 Nov;23(11):1503-1521. doi: 10.1007/s11864-022-01006-7. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36181568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neoadjuvant plus adjuvant combined or sequenced vemurafenib, cobimetinib and atezolizumab in patients with high-risk, resectable BRAF-mutated and wild-type melanoma: NEO-TIM, a phase II randomized non-comparative study.Front Oncol. 2023 Feb 9;13:1107307. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1107307. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36845751 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations in the (Modern) Treatment of Melanoma.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Aug;58(8):1029-1043. doi: 10.1007/s40262-019-00753-5. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 30868471 Review.
-
AKT2 Loss Impairs BRAF-Mutant Melanoma Metastasis.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 12;15(20):4958. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204958. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894325 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to Improve Cancer Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Efficacy, Other Than Abscopal Effect: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Apr 15;11(4):539. doi: 10.3390/cancers11040539. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30991686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kefford R, Arkenau H, Brown MP, Millward M, Infante JR, Long GV, et al. Phase I/II study of GSK2118436, a selective inhibitor of oncogenic mutant BRAF kinase, in patients with metastatic melanoma and other solid tumors. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2010;28:611s.
-
- Atkins MB, Lotze MT, Dutcher JP, Fisher RI, Weiss G, Margolin K, et al. High-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2105–2116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

