Enhanced BRET Technology for the Monitoring of Agonist-Induced and Agonist-Independent Interactions between GPCRs and β-Arrestins
- PMID: 22654789
- PMCID: PMC3356007
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2010.00012
Enhanced BRET Technology for the Monitoring of Agonist-Induced and Agonist-Independent Interactions between GPCRs and β-Arrestins
Abstract
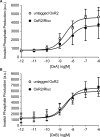
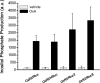
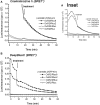
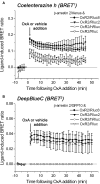
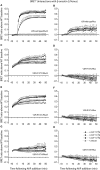
The bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) technique has become extremely valuable for the real-time monitoring of protein-protein interactions in live cells. This method is highly amenable to the detection of G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) interactions with proteins critical for regulating their function, such as β-arrestins. Of particular interest to endocrinologists is the ability to monitor interactions involving endocrine receptors, such as orexin receptor 2 or vasopressin type II receptor. The BRET method utilizes heterologous co-expression of fusion proteins linking one protein of interest (GPCR) to a bioluminescent donor enzyme, a variant of Renilla luciferase, and a second protein of interest (β-arrestin) to an acceptor fluorophore. If in close proximity, energy resulting from oxidation of the coelenterazine substrate by the donor will transfer to the acceptor, which in turn fluoresces. Using novel luciferase constructs, we were able to monitor interactions not detectable using less sensitive BRET combinations in the same configuration. In particular, we were able to show receptor/β-arrestin interactions in an agonist-independent manner using Rluc8-tagged mutant receptors, in contrast to when using Rluc. Therefore, the enhanced BRET methodology has not only enabled live cell compound screening as we have recently published, it now provides a new level of sensitivity for monitoring specific transient, weak or hardly detectable protein-protein complexes, including agonist-independent GPCR/β-arrestin interactions. This has important implications for the use of BRET technologies in endocrine drug discovery programs as well as academic research.
Keywords: G protein-coupled receptor; arrestin; bioluminescence resonance energy transfer; luciferase; orexin; vasopressin.
Figures
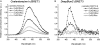
Similar articles
-
Study of GPCR-protein interactions by BRET.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;746:357-71. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-126-0_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21607868
-
Detection of GPCR/beta-arrestin interactions in live cells using bioluminescence resonance energy transfer technology.Methods Mol Biol. 2009;552:305-17. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-317-6_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2009. PMID: 19513659
-
Methods to Monitor the Trafficking of β-Arrestin/G Protein-Coupled Receptor Complexes Using Enhanced Bystander BRET.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1957:59-68. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9158-7_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30919346
-
New technologies: bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) for the detection of real time interactions involving G-protein coupled receptors.Pituitary. 2003;6(3):141-51. doi: 10.1023/b:pitu.0000011175.41760.5d. Pituitary. 2003. PMID: 14974443 Review.
-
NanoBRET: The Bright Future of Proximity-Based Assays.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Mar 26;7:56. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00056. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30972335 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biophysical Detection of Diversity and Bias in GPCR Function.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Mar 5;5:26. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00026. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24634666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of interactions between TLR2, MyD88 and TIRAP by bioluminescence resonance energy transfer is hampered by artefacts of protein overexpression.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 23;13(8):e0202408. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202408. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30138457 Free PMC article.
-
The bile acid receptor TGR5 does not interact with β-arrestins or traffic to endosomes but transmits sustained signals from plasma membrane rafts.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 9;288(32):22942-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.455774. Epub 2013 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23818521 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on neonatal and infantile onset of nephrogenic syndrome of inappropriate antidiuresis: 12 years later.Pediatr Nephrol. 2019 May;34(5):763-775. doi: 10.1007/s00467-018-3922-6. Epub 2018 Mar 15. Pediatr Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 29546600 Review.
-
Agonist-biased trafficking of somatostatin receptor 2A in enteric neurons.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 6;288(36):25689-25700. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.496414. Epub 2013 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23913690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bernier V., Lagace M., Lonergan M., Arthus M. F., Bichet D. G., Bouvier M. (2004). Functional rescue of the constitutively internalized V2 vasopressin receptor mutant R137H by the pharmacological chaperone action of SR49059. Mol. Endocrinol. 18, 2074–2084 - PubMed
-
- Dacres H., Wang J., Dumancic M. M., Trowell S. C. (2010). Experimental determination of the Forster distance for two commonly used bioluminescent resonance energy transfer pairs. Anal. Chem. 82, 432–435 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

