Heterotrimeric G protein-dependent WNT-5A signaling to ERK1/2 mediates distinct aspects of microglia proinflammatory transformation
- PMID: 22647544
- PMCID: PMC3458933
- DOI: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-111
Heterotrimeric G protein-dependent WNT-5A signaling to ERK1/2 mediates distinct aspects of microglia proinflammatory transformation
Abstract
Background: WNT-5A signaling in the central nervous system is important for morphogenesis, neurogenesis and establishment of functional connectivity; the source of WNT-5A and its importance for cellular communication in the adult brain, however, are mainly unknown. We have previously investigated the inflammatory effects of WNT/β-catenin signaling in microglia in Alzheimer's disease. WNT-5A, however, generally recruits β-catenin-independent signaling. Thus, we aim here to characterize the role of WNT-5A and downstream signaling pathways for the inflammatory transformation of the brain's macrophages, the microglia.
Methods: Mouse brain sections were used for immunohistochemistry. Primary isolated microglia and astrocytes were employed to characterize the WNT-induced inflammatory transformation and underlying intracellular signaling pathways by immunoblotting, quantitative mRNA analysis, proliferation and invasion assays. Further, measurements of G protein activation by [γ-(35)S]GTP binding, examination of calcium fluxes and cyclic AMP production were used to define intracellular signaling pathways.
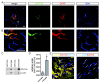
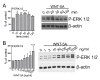
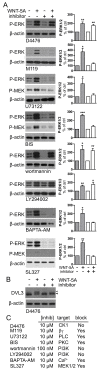
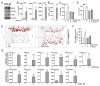
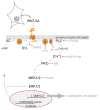
Results: Astrocytes in the adult mouse brain express high levels of WNT-5A, which could serve as a novel astroglia-microglia communication pathway. The WNT-5A-induced proinflammatory microglia response is characterized by increased expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2, cytokines, chemokines, enhanced invasive capacity and proliferation. Mapping of intracellular transduction pathways reveals that WNT-5A activates heterotrimeric G(i/o) proteins to reduce cyclic AMP levels and to activate a G(i/o) protein/phospholipase C/calcium-dependent protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) axis. We show further that WNT-5A-induced ERK1/2 signaling is responsible for distinct aspects of the proinflammatory transformation, such as matrix metalloprotease 9/13 expression, invasion and proliferation.
Conclusions: Thus, WNT-5A-induced and G protein-dependent signaling to ERK1/2 is important for the regulation of proinflammatory responses in mouse primary microglia cells. We show for the first time that WNT-5A/G protein signaling mediates physiologically important processes in primary mammalian cells with natural receptor and G protein stochiometry. Consequently, WNT-5A emerges as an important means of astrocyte-microglia communication and we, therefore, suggest WNT-5A as a new player in neuroinflammatory conditions, such as neurodegenerative disease, hypoxia, stroke, injury and infection.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pertussis toxin-sensitive heterotrimeric G(αi/o) proteins mediate WNT/β-catenin and WNT/ERK1/2 signaling in mouse primary microglia stimulated with purified WNT-3A.Cell Signal. 2013 Apr;25(4):822-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 22. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23266471
-
WNT-5A stimulates the GDP/GTP exchange at pertussis toxin-sensitive heterotrimeric G proteins.Cell Signal. 2011 Mar;23(3):550-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.11.004. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Cell Signal. 2011. PMID: 21070854
-
Recombinant WNTs differentially activate β-catenin-dependent and -independent signalling in mouse microglia-like cells.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011 Nov;203(3):363-72. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.2011.02324.x. Epub 2011 Jun 20. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2011. PMID: 21557822
-
WNT-5A: signaling and functions in health and disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Feb;73(3):567-87. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2076-y. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26514730 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wnt and calcium signaling: beta-catenin-independent pathways.Cell Calcium. 2005 Sep-Oct;38(3-4):439-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2005.06.022. Cell Calcium. 2005. PMID: 16099039 Review.
Cited by
-
WNT-5A triggers Cdc42 activation leading to an ERK1/2 dependent decrease in MMP9 activity and invasive migration of breast cancer cells.Mol Oncol. 2013 Oct;7(5):870-83. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 Apr 28. Mol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23727359 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Biomarkers and Potential Mechanisms of Botulinum Toxin Type A in the Treatment of Microglial Inflammatory Activation through P2X7 Receptors based on Transcriptome Sequencing.Curr Pharm Des. 2024;30(38):3038-3053. doi: 10.2174/0113816128318908240730093036. Curr Pharm Des. 2024. PMID: 39177140
-
Glial gene networks associated with alcohol dependence.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 29;9(1):10949. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47454-4. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31358844 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia-Derived Olfactomedin-like 3 Promotes Pro-Tumorigenic Microglial Function and Malignant Features of Glioma Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 2;22(23):13052. doi: 10.3390/ijms222313052. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884869 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia Polarization, Gene-Environment Interactions and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: Emerging Roles of Glia-Neuron and Glia-Stem/Neuroprogenitor Crosstalk for Dopaminergic Neurorestoration in Aged Parkinsonian Brain.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Feb 12;10:12. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00012. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29483868 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

