The RNA-binding protein CUG-BP1 increases survivin expression in oesophageal cancer cells through enhanced mRNA stability
- PMID: 22646166
- PMCID: PMC4118298
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20120112
The RNA-binding protein CUG-BP1 increases survivin expression in oesophageal cancer cells through enhanced mRNA stability
Abstract
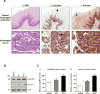
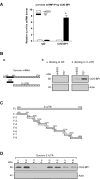
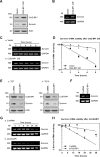
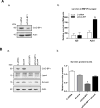
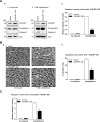
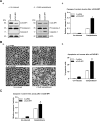
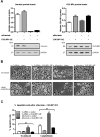
Survivin, a member of the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis protein) family, plays important roles in maintaining cellular homoeostasis and regulating cell-cycle progression. This IAP is overexpressed in oesophageal cancer cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and resistance to apoptosis. CUG-BP1 (CUG-binding protein 1) is an RNA-binding protein that regulates the stability and translational efficiency of target mRNAs. In the present paper, we report that CUG-BP1 is overexpressed in oesophageal cancer cell lines and human oesophageal cancer specimens. CUG-BP1 associates with the 3'-untranslated region of survivin mRNA, thereby stabilizing the transcript and elevating its expression in oesophageal cancer cells. Our results show that overexpression of CUG-BP1 in oesophageal epithelial cells results in increased survivin mRNA stability and consequently survivin protein expression. Conversely, silencing CUG-BP1 in oesophageal cancer cells destabilizes survivin mRNA, lowering the level of survivin protein. In addition, we have found that altering CUG-BP1 expression modulates susceptibility to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Overexpression of CUG-BP1 in oesophageal epithelial cells increases resistance to apoptosis, whereas silencing CUG-BP1 makes oesophageal cancer cells more susceptible to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Co-transfection experiments with small interfering RNA directed against survivin suggest that the anti-apoptotic role for CUG-BP1 is not entirely dependent on its effect on survivin expression.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overexpression of miR-214-3p in esophageal squamous cancer cells enhances sensitivity to cisplatin by targeting survivin directly and indirectly through CUG-BP1.Oncogene. 2016 Apr 21;35(16):2087-97. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.271. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26234674 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein HuR stabilizes survivin mRNA in human oesophageal epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2011 Jul 1;437(1):89-96. doi: 10.1042/BJ20110028. Biochem J. 2011. PMID: 21443519
-
Loss of p53, rather than beta-catenin overexpression, induces survivin-mediated resistance to apoptosis in an esophageal cancer cell line.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010 Jul;140(1):225-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.11.038. Epub 2010 Mar 16. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20236666
-
Coordinate regulation of mRNA decay networks by GU-rich elements and CELF1.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011 Aug;21(4):444-51. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.03.002. Epub 2011 Apr 13. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2011. PMID: 21497082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional regulation of the survivin gene.Mol Biol Rep. 2014 Jan;41(1):233-40. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2856-0. Epub 2013 Nov 7. Mol Biol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24197699 Review.
Cited by
-
Post-transcriptional controls by ribonucleoprotein complexes in the acquisition of drug resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Aug 20;14(8):17204-20. doi: 10.3390/ijms140817204. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23965981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
lncRNA TUG1 as a ceRNA promotes PM exposure-induced airway hyper-reactivity.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Aug 15;416:125878. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125878. Epub 2021 Apr 16. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 34492818 Free PMC article.
-
Increased nuclear but not cytoplasmic activities of CELF1 protein leads to muscle wasting.Hum Mol Genet. 2020 Jun 27;29(10):1729-1744. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddaa095. Hum Mol Genet. 2020. PMID: 32412585 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Binding Proteins in Intestinal Epithelial Biology and Colorectal Cancer.Trends Mol Med. 2018 May;24(5):490-506. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.03.008. Epub 2018 Apr 5. Trends Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29627433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression of CUGBP1 After Spinal Cord Injury in Rats.Neurochem Res. 2015 Sep;40(9):1966-75. doi: 10.1007/s11064-015-1692-0. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Neurochem Res. 2015. PMID: 26283512
References
-
- Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:212–236. - PubMed
-
- Chang E, Donahue J, Smith A, Hornick J, Rao JN, Wang JY, Battafarano RJ. Loss of p53, rather than beta-catenin overexpression, induces survivin-mediated resistance to apoptosis in an esophageal cancer cell line. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Li F, Ambrosini G, Chu EY, Plescia J, Tognin S, Marchisio PC, Altieri DC. Control of apoptosis and mitotic spindle checkpoint by survivin. Nature. 1998;396:580–584. - PubMed
-
- Ikeguchi M, Yamaguchi K, Kaibara N. Survivin gene expression positively correlates with proliferative activity of cancer cells in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2003;24:40–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

