Functional dissociation between PIKfyve-synthesized PtdIns5P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 by means of the PIKfyve inhibitor YM201636
- PMID: 22621786
- PMCID: PMC3422984
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00105.2012
Functional dissociation between PIKfyve-synthesized PtdIns5P and PtdIns(3,5)P2 by means of the PIKfyve inhibitor YM201636
Abstract
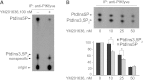
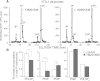
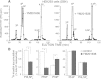
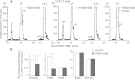
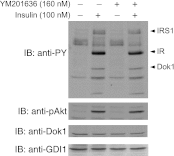
PIKfyve is an essential mammalian lipid kinase with pleiotropic cellular functions whose genetic knockout in mice leads to preimplantation lethality. Despite several reports for PIKfyve-catalyzed synthesis of phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate (PtdIns5P) along with phosphatidylinositol-3,5-biphosphate [PtdIns(3,5)P(2)] in vitro and in vivo, the role of the PIKfyve pathway in intracellular PtdIns5P production remains underappreciated and the function of the PIKfyve-synthesized PtdIns5P pool poorly characterized. Hence, the recently discovered potent PIKfyve-selective inhibitor, the YM201636 compound, has been solely tested for inhibiting PtdIns(3,5)P(2) synthesis. Here, we have compared the in vitro and in vivo inhibitory potency of YM201636 toward PtdIns5P and PtdIns(3,5)P(2). Unexpectedly, we observed that at low doses (10-25 nM), YM201636 inhibited preferentially PtdIns5P rather than PtdIns(3,5)P(2) production in vitro, whereas at higher doses, the two products were similarly inhibited. In cellular contexts, YM201636 at 160 nM inhibited PtdIns5P synthesis twice more effectively compared with PtdIns(3,5)P(2) synthesis. In 3T3L1 adipocytes, human embryonic kidney 293 and Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-T) cells, levels of PtdIns5P dropped by 62-71% of the corresponding untreated controls, whereas those of PtdIns(3,5)P(2) fell by only 28-46%. The preferential inhibition of PtdIns5P versus PtdIns(3,5)P(2) at low doses of YM201636 was explored to probe contributions of the PIKfyve-catalyzed PtdIns5P pool to insulin-induced actin stress fiber disassembly in CHO-T cells, GLUT4 translocation in 3T3L1 adipocytes, and induction of aberrant cellular vacuolation in these or other cell types. The results provide the first experimental evidence that the principal pathway for PtdIns5P intracellular production is through PIKfyve and that insulin effect on actin stress fiber disassembly is mediated entirely by the PIKfyve-produced PtdIns5P pool.
Figures

Similar articles
-
YM201636, an inhibitor of retroviral budding and PIKfyve-catalyzed PtdIns(3,5)P2 synthesis, halts glucose entry by insulin in adipocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 May 8;382(3):566-70. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.03.063. Epub 2009 Mar 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19289105 Free PMC article.
-
Active vacuolar H+ ATPase and functional cycle of Rab5 are required for the vacuolation defect triggered by PtdIns(3,5)P2 loss under PIKfyve or Vps34 deficiency.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016 Sep 1;311(3):C366-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00104.2016. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27335171 Free PMC article.
-
Role for a novel signaling intermediate, phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate, in insulin-regulated F-actin stress fiber breakdown and GLUT4 translocation.Endocrinology. 2004 Nov;145(11):4853-65. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-0489. Epub 2004 Jul 29. Endocrinology. 2004. PMID: 15284192
-
Small molecule PIKfyve inhibitors as cancer therapeutics: Translational promises and limitations.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Nov 15;383:114771. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114771. Epub 2019 Oct 16. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31628917 Review.
-
PtdIns5P: news and views of its appearance, disappearance and deeds.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013 Oct 15;538(2):171-80. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2013.07.023. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2013. PMID: 23916588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polyphosphoinositide binding domains: Key to inositol lipid biology.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):746-58. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.013. Epub 2015 Feb 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25732852 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo, Pikfyve generates PI(3,5)P2, which serves as both a signaling lipid and the major precursor for PI5P.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Oct 23;109(43):17472-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203106109. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 23047693 Free PMC article.
-
The PIKfyve complex regulates the early melanosome homeostasis required for physiological amyloid formation.J Cell Sci. 2019 Feb 28;132(5):jcs229500. doi: 10.1242/jcs.229500. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 30709920 Free PMC article.
-
cdc-like/dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylation-regulated kinases inhibitor leucettine L41 induces mTOR-dependent autophagy: implication for Alzheimer's disease.Mol Pharmacol. 2014 Mar;85(3):441-50. doi: 10.1124/mol.113.090837. Epub 2013 Dec 23. Mol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24366666 Free PMC article.
-
Lysosome enlargement during inhibition of the lipid kinase PIKfyve proceeds through lysosome coalescence.J Cell Sci. 2018 May 21;131(10):jcs213587. doi: 10.1242/jcs.213587. J Cell Sci. 2018. PMID: 29661845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Astle MV, Seaton G, Davies EM, Fedele CG, Rahman P, Arsala L, Mitchell CA. Regulation of phosphoinositide signaling by the inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatases. IUBMB Life 58: 451–456, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Carpenter CL. Cantley Phosphoinositide kinases LC Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 153–158, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Coronas S, Lagarrigue F, Ramel D, Chicanne G, Delsol G, Payrastre B, Tronchere H. Elevated levels of PtdIns5P in NPM-ALK transformed cells: implication of PIKfyve. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372: 351–355, 2008 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

