Mechanism of nucleic acid unwinding by SARS-CoV helicase
- PMID: 22615777
- PMCID: PMC3352918
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036521
Mechanism of nucleic acid unwinding by SARS-CoV helicase
Abstract
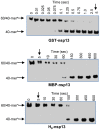
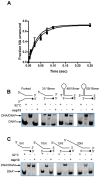
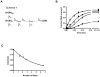
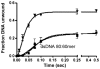
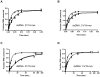
The non-structural protein 13 (nsp13) of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (SARS-CoV) is a helicase that separates double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) or DNA (dsDNA) with a 5' → 3' polarity, using the energy of nucleotide hydrolysis. We determined the minimal mechanism of helicase function by nsp13. We showed a clear unwinding lag with increasing length of the double-stranded region of the nucleic acid, suggesting the presence of intermediates in the unwinding process. To elucidate the nature of the intermediates we carried out transient kinetic analysis of the nsp13 helicase activity. We demonstrated that the enzyme unwinds nucleic acid in discrete steps of 9.3 base-pairs (bp) each, with a catalytic rate of 30 steps per second. Therefore the net unwinding rate is ~280 base-pairs per second. We also showed that nsp12, the SARS-CoV RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), enhances (2-fold) the catalytic efficiency of nsp13 by increasing the step size of nucleic acid (RNA/RNA or DNA/DNA) unwinding. This effect is specific for SARS-CoV nsp12, as no change in nsp13 activity was observed when foot-and-mouth-disease virus RdRp was used in place of nsp12. Our data provide experimental evidence that nsp13 and nsp12 can function in a concerted manner to improve the efficiency of viral replication and enhance our understanding of nsp13 function during SARS-CoV RNA synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
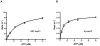
Similar articles
-
Structural and biochemical basis for the difference in the helicase activity of two different constructs of SARS-CoV helicase.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2012 Dec 22;58(1):114-21. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2012. PMID: 23273200 Free PMC article.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus replication inhibitor that interferes with the nucleic acid unwinding of the viral helicase.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Sep;56(9):4718-28. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00957-12. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22733076 Free PMC article.
-
A high ATP concentration enhances the cooperative translocation of the SARS coronavirus helicase nsP13 in the unwinding of duplex RNA.Sci Rep. 2020 Mar 11;10(1):4481. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61432-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32161317 Free PMC article.
-
Development of chemical inhibitors of the SARS coronavirus: viral helicase as a potential target.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Nov 15;84(10):1351-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.08.012. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22935448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synthesis of novel test compounds for antiviral chemotherapy of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).Curr Med Chem. 2005;12(18):2095-162. doi: 10.2174/0929867054637644. Curr Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16101496 Review.
Cited by
-
Current approaches for target-specific drug discovery using natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Virus Res. 2020 Dec;290:198169. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198169. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32979476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetic Engineering Systems to Study Human Viral Pathogens from the Coronaviridae Family.Mol Biol. 2022;56(1):72-89. doi: 10.1134/S0026893322010022. Epub 2022 Feb 12. Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35194246 Free PMC article.
-
Lessons Learnt from COVID-19: Computational Strategies for Facing Present and Future Pandemics.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 23;24(5):4401. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054401. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36901832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural biology of SARS-CoV-2: open the door for novel therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jan 27;7(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-00884-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35087058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus protein complex integrates processive RNA polymerase and exonuclease activities.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Sep 16;111(37):E3900-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323705111. Epub 2014 Sep 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 25197083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marra MA, Jones SJ, Astell CR, Holt RA, Brooks-Wilson A, et al. The Genome sequence of the SARS-associated coronavirus. Science. 2003;300:1399–1404. - PubMed
-
- Rota PA, Oberste MS, Monroe SS, Nix WA, Campagnoli R, et al. Characterization of a novel coronavirus associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Science. 2003;300:1394–1399. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

