Molecular insights into the function of RING finger (RNF)-containing proteins hRNF8 and hRNF168 in Ubc13/Mms2-dependent ubiquitylation
- PMID: 22589545
- PMCID: PMC3390666
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.359653
Molecular insights into the function of RING finger (RNF)-containing proteins hRNF8 and hRNF168 in Ubc13/Mms2-dependent ubiquitylation
Abstract
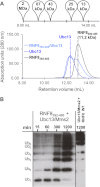
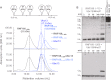
The repair of DNA double strand breaks by homologous recombination relies on the unique topology of the chains formed by Lys-63 ubiquitylation of chromatin to recruit repair factors such as breast cancer 1 (BRCA1) to sites of DNA damage. The human RING finger (RNF) E3 ubiquitin ligases, RNF8 and RNF168, with the E2 ubiquitin-conjugating complex Ubc13/Mms2, perform the majority of Lys-63 ubiquitylation in homologous recombination. Here, we show that RNF8 dimerizes and binds to Ubc13/Mms2, thereby stimulating formation of Lys-63 ubiquitin chains, whereas the related RNF168 RING domain is a monomer and does not catalyze Lys-63 polyubiquitylation. The crystal structure of the RNF8/Ubc13/Mms2 ternary complex reveals the structural basis for the interaction between Ubc13 and the RNF8 RING and that an extended RNF8 coiled-coil is responsible for its dimerization. Mutations that disrupt the RNF8/Ubc13 binding surfaces, or that truncate the RNF8 coiled-coil, reduce RNF8-catalyzed ubiquitylation. These findings support the hypothesis that RNF8 is responsible for the initiation of Lys-63-linked ubiquitylation in the DNA damage response, which is subsequently amplified by RNF168.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNF8 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Stimulates Ubc13 E2 Conjugating Activity That Is Essential for DNA Double Strand Break Signaling and BRCA1 Tumor Suppressor Recruitment.J Biol Chem. 2016 Apr 29;291(18):9396-410. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715698. Epub 2016 Feb 22. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26903517 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for role of ring finger protein RNF168 RING domain.Cell Cycle. 2013 Jan 15;12(2):312-21. doi: 10.4161/cc.23104. Epub 2012 Jan 15. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23255131 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H1 couples initiation and amplification of ubiquitin signalling after DNA damage.Nature. 2015 Nov 19;527(7578):389-93. doi: 10.1038/nature15401. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26503038
-
Opposing roles of RNF8/RNF168 and deubiquitinating enzymes in ubiquitination-dependent DNA double-strand break response signaling and DNA-repair pathway choice.J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i33-i40. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw027. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26983989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory ubiquitylation in response to DNA double-strand breaks.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Apr 5;8(4):436-43. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.01.013. Epub 2009 Feb 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19230794 Review.
Cited by
-
Covalent Inhibition of Ubc13 Affects Ubiquitin Signaling and Reveals Active Site Elements Important for Targeting.ACS Chem Biol. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):1718-28. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.5b00222. Epub 2015 May 1. ACS Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 25909880 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric activation of the RNF146 ubiquitin ligase by a poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation signal.Nature. 2015 Jan 8;517(7533):223-6. doi: 10.1038/nature13826. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Nature. 2015. PMID: 25327252 Free PMC article.
-
Structural mechanisms underlying signaling in the cellular response to DNA double strand breaks.Mutat Res. 2013 Oct;750(1-2):15-22. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Jul 27. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23896398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Basis for K63-Linked Ubiquitination Processes in Double-Strand DNA Break Repair: A Focus on Kinetics and Dynamics.J Mol Biol. 2017 Nov 10;429(22):3409-3429. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.05.029. Epub 2017 Jun 3. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28587922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NDRG1 facilitates lytic replication of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus by maintaining the stability of the KSHV helicase.PLoS Pathog. 2021 Jun 2;17(6):e1009645. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009645. eCollection 2021 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2021. PMID: 34077484 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lukas J., Lukas C., Bartek J. (2011) More than just a focus: the chromatin response to DNA damage and its role in genome integrity maintenance. Nat. Cell Biol. 13, 1161–1169 - PubMed
-
- Stucki M., Clapperton J. A., Mohammad D., Yaffe M. B., Smerdon S. J., Jackson S. P. (2005) MDC1 directly binds phosphorylated histone H2AX to regulate cellular responses to DNA double-strand breaks. Cell 123, 1213–1226 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

