SIRT1 negatively regulates the activities, functions, and protein levels of hMOF and TIP60
- PMID: 22586264
- PMCID: PMC3416197
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00496-12
SIRT1 negatively regulates the activities, functions, and protein levels of hMOF and TIP60
Abstract
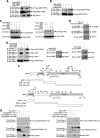
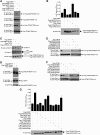
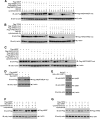
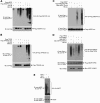
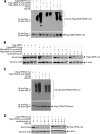
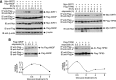
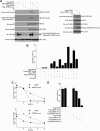
SIRT1 is a NAD(+)-dependent histone H4K16 deacetylase that controls several different normal physiologic and disease processes. Like most histone deacetylases, SIRT1 also deacetylates nonhistone proteins. Here, we show that two members of the MYST (MOZ, Ybf2/Sas3, Sas2, and TIP60) acetyltransferase family, hMOF and TIP60, are SIRT1 substrates. SIRT1 deacetylation of the enzymatic domains of hMOF and TIP60 inhibits their acetyltransferase activity and promotes ubiquitination-dependent degradation of these proteins. Importantly, immediately following DNA damage, the binding of SIRT1 to hMOF and TIP60 is transiently interrupted, with corresponding hMOF/TIP60 hyperacetylation. Lysine-to-arginine mutations in SIRT1-targeted lysines on hMOF and TIP60 repress DNA double-strand break repair and inhibit the ability of hMOF/TIP60 to induce apoptosis in response to DNA double-strand break. Together, these findings uncover novel pathways in which SIRT1 dynamically interacts with and regulates hMOF and TIP60 through deacetylation and provide additional mechanistic insights by which SIRT1 regulates DNA damage response.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of histone acetyltransferase TIP60 function by histone deacetylase 3.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 5;289(49):33878-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.575266. Epub 2014 Oct 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25301942 Free PMC article.
-
Sirt1 physically interacts with Tip60 and negatively regulates Tip60-mediated acetylation of H2AX.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Dec 25;390(4):1355-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.156. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19895790
-
Modulations of hMOF autoacetylation by SIRT1 regulate hMOF recruitment and activities on the chromatin.Cell Res. 2011 Aug;21(8):1182-95. doi: 10.1038/cr.2011.71. Epub 2011 Apr 19. Cell Res. 2011. PMID: 21502975 Free PMC article.
-
Role of histone acetyltransferases MOF and Tip60 in genome stability.DNA Repair (Amst). 2021 Nov;107:103205. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2021.103205. Epub 2021 Aug 8. DNA Repair (Amst). 2021. PMID: 34399315 Review.
-
The Functional Analysis of Histone Acetyltransferase MOF in Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jan 14;17(1):99. doi: 10.3390/ijms17010099. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26784169 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
NAD(+)-SIRT1 control of H3K4 trimethylation through circadian deacetylation of MLL1.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;22(4):312-8. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2990. Epub 2015 Mar 9. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25751424 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Cellular Roles of the Lysine Acetyltransferase Tip60 in Cancer: A Multi-Action Molecular Target for Precision Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;16(15):2677. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152677. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NeuroHeal Reduces Muscle Atrophy and Modulates Associated Autophagy.Cells. 2020 Jun 28;9(7):1575. doi: 10.3390/cells9071575. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32605216 Free PMC article.
-
Role of SIRT1 in Chemoresistant Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 23;24(19):14470. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914470. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37833921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A PARP1-BRG1-SIRT1 axis promotes HR repair by reducing nucleosome density at DNA damage sites.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Sep 19;47(16):8563-8580. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz592. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31291457 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akhtar A, Becker PB. 2000. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol. Cell 5:367–375 - PubMed
-
- Avvakumov N, Cote J. 2007. The MYST family of histone acetyltransferases and their intimate links to cancer. Oncogene 26:5395–5407 - PubMed
-
- Blander G, Guarente L. 2004. The Sir2 family of protein deacetylases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 73:417–435 - PubMed
-
- Bouras T, et al. 2005. SIRT1 deacetylation and repression of p300 involves lysine residues 1020/1024 within the cell cycle regulatory domain 1. J. Biol. Chem. 280:10264–10276 - PubMed
-
- Brunet A, et al. 2004. Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303:2011–2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
