BEDOPS: high-performance genomic feature operations
- PMID: 22576172
- PMCID: PMC3389768
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts277
BEDOPS: high-performance genomic feature operations
Abstract
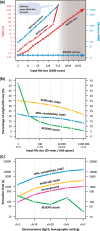
The large and growing number of genome-wide datasets highlights the need for high-performance feature analysis and data comparison methods, in addition to efficient data storage and retrieval techniques. We introduce BEDOPS, a software suite for common genomic analysis tasks which offers improved flexibility, scalability and execution time characteristics over previously published packages. The suite includes a utility to compress large inputs into a lossless format that can provide greater space savings and faster data extractions than alternatives.
Availability: http://code.google.com/p/bedops/ includes binaries, source and documentation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Operating on Genomic Ranges Using BEDOPS.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1418:267-81. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3578-9_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27008020
-
MAFCO: a compression tool for MAF files.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 27;10(3):e0116082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116082. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25816229 Free PMC article.
-
BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features.Bioinformatics. 2010 Mar 15;26(6):841-2. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq033. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Bioinformatics. 2010. PMID: 20110278 Free PMC article.
-
SeqArray-a storage-efficient high-performance data format for WGS variant calls.Bioinformatics. 2017 Aug 1;33(15):2251-2257. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx145. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28334390 Free PMC article.
-
When the levee breaks: a practical guide to sketching algorithms for processing the flood of genomic data.Genome Biol. 2019 Sep 13;20(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s13059-019-1809-x. Genome Biol. 2019. PMID: 31519212 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic identification of post-transcriptional regulatory modules.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 9;15(1):7872. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52215-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39251607 Free PMC article.
-
PML is a constitutive component of chromatin domains enriched in repetitive elements and duplicated gene clusters in cancer cells.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 17;10(17):e36499. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36499. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39263139 Free PMC article.
-
Mediator binding to UASs is broadly uncoupled from transcription and cooperative with TFIID recruitment to promoters.EMBO J. 2016 Nov 15;35(22):2435-2446. doi: 10.15252/embj.201695020. Epub 2016 Oct 20. EMBO J. 2016. PMID: 27797823 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of long-read sequencing technologies in interrogating bacteria and fly genomes.G3 (Bethesda). 2021 Jun 17;11(6):jkab083. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkab083. G3 (Bethesda). 2021. PMID: 33768248 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleation of DNA repair factors by FOXA1 links DNA demethylation to transcriptional pioneering.Nat Genet. 2016 Sep;48(9):1003-13. doi: 10.1038/ng.3635. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Nat Genet. 2016. PMID: 27500525
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

